GI-type T4SS-mediated horizontal transfer of the 89K pathogenicity island in epidemic Streptococcus suis serotype 2
- PMID: 21244532
- PMCID: PMC3132442
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2011.07553.x
GI-type T4SS-mediated horizontal transfer of the 89K pathogenicity island in epidemic Streptococcus suis serotype 2
Abstract
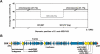
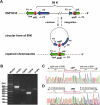
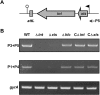
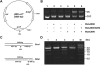
Pathogenicity islands (PAIs), a distinct type of genomic island (GI), play important roles in the rapid adaptation and increased virulence of pathogens. 89K is a newly identified PAI in epidemic Streptococcus suis isolates that are related to the two recent large-scale outbreaks of human infection in China. However, its mechanism of evolution and contribution to the epidemic spread of S. suis 2 remain unknown. In this study, the potential for mobilization of 89K was evaluated, and its putative transfer mechanism was investigated. We report that 89K can spontaneously excise to form an extrachromosomal circular product. The precise excision is mediated by an 89K-borne integrase through site-specific recombination, with help from an excisionase. The 89K excision intermediate acts as a substrate for lateral transfer to non-89K S. suis 2 recipients, where it reintegrates site-specifically into the target site. The conjugal transfer of 89K occurred via a GI type IV secretion system (T4SS) encoded in 89K, at a frequency of 10(-6) transconjugants per donor. This is the first demonstration of horizontal transfer of a Gram-positive PAI mediated by a GI-type T4SS. We propose that these genetic events are important in the emergence, pathogenesis and persistence of epidemic S. suis 2 strains.
© 2011 Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A functional peptidoglycan hydrolase characterized from T4SS in 89K pathogenicity island of epidemic Streptococcus suis serotype 2.BMC Microbiol. 2014 Mar 22;14:73. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-14-73. BMC Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24655418 Free PMC article.
-
Role of a type IV-like secretion system of Streptococcus suis 2 in the development of streptococcal toxic shock syndrome.J Infect Dis. 2011 Jul 15;204(2):274-81. doi: 10.1093/infdis/jir261. J Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21673039
-
Loss of 89K Pathogenicity Island in Epidemic Streptococcus suis, China.Emerg Infect Dis. 2016 Jun;22(6):1126-7. doi: 10.3201/eid2206.152010. Emerg Infect Dis. 2016. PMID: 27192444 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Uncovering newly emerging variants of Streptococcus suis, an important zoonotic agent.Trends Microbiol. 2010 Mar;18(3):124-31. doi: 10.1016/j.tim.2009.12.003. Epub 2010 Jan 12. Trends Microbiol. 2010. PMID: 20071175 Review.
-
Pathogenicity island integrase cross-talk: a potential new tool for virulence modulation.Mol Microbiol. 2006 Aug;61(3):555-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2958.2006.05262.x. Mol Microbiol. 2006. PMID: 16879637 Review.
Cited by
-
The 2.5 Å structure of the enterococcus conjugation protein TraM resembles VirB8 type IV secretion proteins.J Biol Chem. 2013 Jan 18;288(3):2018-28. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.428847. Epub 2012 Nov 27. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23188825 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism and Function of Type IV Secretion During Infection of the Human Host.Microbiol Spectr. 2016 Jun;4(3):10.1128/microbiolspec.VMBF-0024-2015. doi: 10.1128/microbiolspec.VMBF-0024-2015. Microbiol Spectr. 2016. PMID: 27337453 Free PMC article. Review.
-
ICESsuHN105, a Novel Multiple Antibiotic Resistant ICE in Streptococcus suis Serotype 5 Strain HN105.Front Microbiol. 2019 Feb 26;10:274. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2019.00274. eCollection 2019. Front Microbiol. 2019. PMID: 30863372 Free PMC article.
-
PrgK, a multidomain peptidoglycan hydrolase, is essential for conjugative transfer of the pheromone-responsive plasmid pCF10.J Bacteriol. 2014 Feb;196(3):527-39. doi: 10.1128/JB.00950-13. Epub 2013 Nov 15. J Bacteriol. 2014. PMID: 24244005 Free PMC article.
-
Pseudomonas aeruginosa MutL promotes large chromosomal deletions through non-homologous end joining to prevent bacteriophage predation.Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 May 18;46(9):4505-4514. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky160. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018. PMID: 29514250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bowden DW, Modrich P. In vitro maturation of circular bacteriophage P2 DNA. Purification of ter components and characterization of the reaction. J Biol Chem. 1985;260:6999–7007. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

