Separating instability from aggregation propensity in γS-crystallin variants
- PMID: 21244846
- PMCID: PMC3021659
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpj.2010.12.3691
Separating instability from aggregation propensity in γS-crystallin variants
Abstract
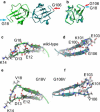
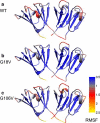
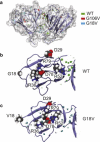
Molecular dynamics (MD) simulations, circular dichroism (CD), and dynamic light scattering (DLS) measurements were used to investigate the aggregation propensity of the eye-lens protein γS-crystallin. The wild-type protein was investigated along with the cataract-related G18V variant and the symmetry-related G106V variant. The MD simulations suggest that local sequence differences result in dramatic differences in dynamics and hydration between these two apparently similar point mutations. This finding is supported by the experimental measurements, which show that although both variants appear to be mostly folded at room temperature, both display increased aggregation propensity. Although the disease-related G18V variant is not the most strongly destabilized, it aggregates more readily than either the wild-type or the G106V variant. These results indicate that γS-crystallin provides an excellent model system for investigating the role of dynamics and hydration in aggregation by locally unfolded proteins.
Copyright © 2011 Biophysical Society. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Chiti F., Dobson C.M. Protein misfolding, functional amyloid, and human disease. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2006;75:333–366. - PubMed
-
- Booth D.R., Sunde M., Pepys M.B. Instability, unfolding and aggregation of human lysozyme variants underlying amyloid fibrillogenesis. Nature. 1997;385:787–793. - PubMed
-
- Pepys M.B., Hawkins P.N., Hsuan J.J. Human lysozyme gene mutations cause hereditary systemic amyloidosis. Nature. 1993;362:553–557. - PubMed
-
- Liemann S., Glockshuber R. Influence of amino acid substitutions related to inherited human prion diseases on the thermodynamic stability of the cellular prion protein. Biochemistry. 1999;38:3258–3267. - PubMed
-
- Caughey B., Lansbury P.T. Protofibrils, pores, fibrils, and neurodegeneration: separating the responsible protein aggregates from the innocent bystanders. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2003;26:267–298. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

