Functional activation of the estrogen receptor-α and aromatase by the HDAC inhibitor entinostat sensitizes ER-negative tumors to letrozole
- PMID: 21245100
- PMCID: PMC3076193
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-2458
Functional activation of the estrogen receptor-α and aromatase by the HDAC inhibitor entinostat sensitizes ER-negative tumors to letrozole
Abstract
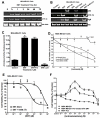
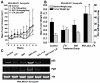
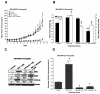
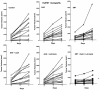
Approximately 25% of breast cancers do not express the estrogen receptor-α (ERα) and consequently do not respond to endocrine therapy. In these tumors, ERα repression is often due to epigenetic modifications such as methylation and histone deacetylation. For this reason, we investigated the ability of the histone deacetylase inhibitor entinostat (ENT) to trigger reexpression of ERα and aromatase in breast cancer cells, with the notion that this treatment would restore sensitivity to the aromatase inhibitor (AI) letrozole. ENT treatment of tumor cells increased expression of ERα and aromatase, along with the enzymatic activity of aromatase, in a dose-dependent manner both in vitro and in vivo. Notably, ERα and aromatase upregulation resulted in sensitization of breast cancer cells to estrogen and letrozole. Tumor growth rate was significantly lower in tumor xenografts following treatment with ENT alone and in combination with letrozole than in control tumors (P > 0.001). ENT plus letrozole also prevented lung colonization and growth of tumor cells, with a significant reduction (P > 0.03) in both visible and microscopic foci. Our results show that ENT treatment can be used to restore the letrozole responsiveness of ER-negative tumors. More generally, they provide a strong rationale for immediate clinical evaluation of combinations of histone deacetylase and aromatase inhibitors to treat ER-negative and endocrine-resistant breast cancers.
©2011 AACR.
Figures


References
-
- Goss PE, Muss HB, Ingle JN, Whelan TJ, Wu M. Extended adjuvant endocrine therapy in breast cancer: current status and future directions. Clinical breast cancer. 2008;8(5):411–7. - PubMed
-
- Swain SM. Aromatase inhibitors--a triumph of translational oncology. N Engl J Med. 2005;353(26):2807–9. - PubMed
-
- Giacinti L, Claudio PP, Lopez M, Giordano A. Epigenetic information and estrogen receptor alpha expression in breast cancer. The oncologist. 2006;11(1):1–8. - PubMed
-
- Yang X, Ferguson AT, Nass SJ, et al. Transcriptional activation of estrogen receptor alpha in human breast cancer cells by histone deacetylase inhibition. Cancer Res. 2000;60(24):6890–4. - PubMed
-
- Ottaviano YL, Issa JP, Parl FF, et al. Methylation of the estrogen receptor gene CpG island marks loss of estrogen receptor expression in human breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 1994;54(10):2552–5. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

