Endurance factors improve hippocampal neurogenesis and spatial memory in mice
- PMID: 21245211
- PMCID: PMC3032576
- DOI: 10.1101/lm.2001611
Endurance factors improve hippocampal neurogenesis and spatial memory in mice
Abstract
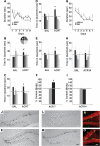
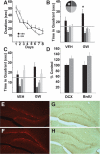
Physical activity improves learning and hippocampal neurogenesis. It is unknown whether compounds that increase endurance in muscle also enhance cognition. We investigated the effects of endurance factors, peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor δ agonist GW501516 and AICAR, activator of AMP-activated protein kinase on memory and neurogenesis. Mice were injected with GW for 7 d or AICAR for 7 or 14 d. Two weeks thereafter mice were tested in the Morris water maze. AICAR (7 d) and GW improved spatial memory. Moreover, AICAR significantly, and GW modestly, elevated dentate gyrus neurogenesis. Thus, pharmacological activation of skeletal muscle may mediate cognitive effects.
Figures
References
-
- Akerström TC, Pedersen BK 2007. Strategies to enhance immune function for marathon runners: What can be done? Sports Med 37: 416–419 - PubMed
-
- Brown JP, Couillard-Després S, Cooper-Kuhn CM, Winkler J, Aigner L, Kuhn HG 2003. Transient expression of double-cortin during adult neurogenesis. J Comp Neurol 467: 1–10 - PubMed
-
- Cimini A, Cerù MP 2008. Emerging roles of peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (PPARs) in the regulation of neural stem cells proliferation and differentiation. Stem Cell Rev 4: 293–303 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
