Blockade of TNF-α rapidly inhibits pain responses in the central nervous system
- PMID: 21245297
- PMCID: PMC3048151
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1011774108
Blockade of TNF-α rapidly inhibits pain responses in the central nervous system
Abstract
There has been a consistent gap in understanding how TNF-α neutralization affects the disease state of arthritis patients so rapidly, considering that joint inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis is a chronic condition with structural changes. We thus hypothesized that neutralization of TNF-α acts through the CNS before directly affecting joint inflammation. Through use of functional MRI (fMRI), we demonstrate that within 24 h after neutralization of TNF-α, nociceptive CNS activity in the thalamus and somatosensoric cortex, but also the activation of the limbic system, is blocked. Brain areas showing blood-oxygen level-dependent signals, a validated method to assess neuronal activity elicited by pain, were significantly reduced as early as 24 h after an infusion of a monoclonal antibody to TNF-α. In contrast, clinical and laboratory markers of inflammation, such as joint swelling and acute phase reactants, were not affected by anti-TNF-α at these early time points. Moreover, arthritic mice overexpressing human TNF-α showed an altered pain behavior and a more intensive, widespread, and prolonged brain activity upon nociceptive stimuli compared with wild-type mice. Similar to humans, these changes, as well as the rewiring of CNS activity resulting in tight clustering in the thalamus, were rapidly reversed after neutralization of TNF-α. These results suggest that neutralization of TNF-α affects nociceptive brain activity in the context of arthritis, long before it achieves anti-inflammatory effects in the joints.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


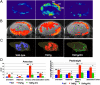
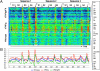
Comment in
-
Mapping the immunological homunculus.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Mar 1;108(9):3461-2. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1100329108. Epub 2011 Feb 22. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21368214 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Does functional MRI convincingly explain the fast effect of TNF-alpha blockade?Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Aug 9;108(32):E412; author reply E413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1106138108. Epub 2011 Jul 28. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21799115 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Smolen JS, Steiner G. Therapeutic strategies for rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2003;2:473–488. - PubMed
-
- Firestein GS. Evolving concepts of rheumatoid arthritis. Nature. 2003;423:356–361. - PubMed
-
- McInnes IB, Schett G. Cytokines in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:429–442. - PubMed
-
- Brennan FM, Jackson A, Chantry D, Maini R, Feldmann M. Inhibitory effect of TNFa antibodies on synovial cell interleukin-1 production in rheumatoid arthritis. Lancet. 1989;334:244–247. - PubMed
-
- Dinarello CA. IL-1: Discoveries, controversies and future directions. Eur J Immunol. 2010;40:599–606. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

