An engineered cardiac reporter cell line identifies human embryonic stem cell-derived myocardial precursors
- PMID: 21245908
- PMCID: PMC3014940
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016004
An engineered cardiac reporter cell line identifies human embryonic stem cell-derived myocardial precursors
Abstract
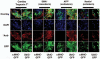
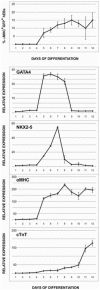
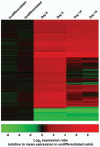
Unlike some organs, the heart is unable to repair itself after injury. Human embryonic stem cells (hESCs) grow and divide indefinitely while maintaining the potential to develop into many tissues of the body. As such, they provide an unprecedented opportunity to treat human diseases characterized by tissue loss. We have identified early myocardial precursors derived from hESCs (hMPs) using an α-myosin heavy chain (αMHC)-GFP reporter line. We have demonstrated by immunocytochemistry and quantitative real-time PCR (qPCR) that reporter activation is restricted to hESC-derived cardiomyocytes (CMs) differentiated in vitro, and that hMPs give rise exclusively to muscle in an in vivo teratoma formation assay. We also demonstrate that the reporter does not interfere with hESC genomic stability. Importantly, we show that hMPs give rise to atrial, ventricular and specialized conduction CM subtypes by qPCR and microelectrode array analysis. Expression profiling of hMPs over the course of differentiation implicate Wnt and transforming growth factor-β signaling pathways in CM development. The identification of hMPs using this αMHC-GFP reporter line will provide important insight into the pathways regulating human myocardial development, and may provide a novel therapeutic reagent for the treatment of cardiac disease.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures




Similar articles
-
Treatment with hESC-Derived Myocardial Precursors Improves Cardiac Function after a Myocardial Infarction.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 31;10(7):e0131123. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131123. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26230835 Free PMC article.
-
Stiff matrix induces switch to pure β-cardiac myosin heavy chain expression in human ESC-derived cardiomyocytes.Basic Res Cardiol. 2016 Nov;111(6):68. doi: 10.1007/s00395-016-0587-9. Epub 2016 Oct 14. Basic Res Cardiol. 2016. PMID: 27743117
-
Primitive cardiac cells from human embryonic stem cells.Stem Cells Dev. 2012 Jun 10;21(9):1513-23. doi: 10.1089/scd.2011.0254. Epub 2011 Nov 9. Stem Cells Dev. 2012. PMID: 21933026
-
Cardiac specific differentiation of mouse embryonic stem cells.Cardiovasc Res. 2003 May 1;58(2):278-91. doi: 10.1016/s0008-6363(03)00248-7. Cardiovasc Res. 2003. PMID: 12757863 Review.
-
A molecular basis for human embryonic stem cell pluripotency.Stem Cell Rev. 2005;1(2):111-8. doi: 10.1385/SCR:1:2:111. Stem Cell Rev. 2005. PMID: 17142845 Review.
Cited by
-
MicroRNAs: a new piece in the paediatric cardiovascular disease puzzle.Cardiol Young. 2013 Oct;23(5):642-55. doi: 10.1017/S1047951113000048. Epub 2013 Feb 26. Cardiol Young. 2013. PMID: 23443043 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human stem cells from single blastomeres reveal pathways of embryonic or trophoblast fate specification.Development. 2015 Dec 1;142(23):4010-25. doi: 10.1242/dev.122846. Epub 2015 Oct 19. Development. 2015. PMID: 26483210 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-363 negatively regulates the left ventricular determining transcription factor HAND1 in human embryonic stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014 Jun 6;5(3):75. doi: 10.1186/scrt464. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2014. PMID: 24906886 Free PMC article.
-
Fast and efficient multitransgenic modification of human pluripotent stem cells.Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2014 Apr;25(2):136-53. doi: 10.1089/hgtb.2012.248. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Hum Gene Ther Methods. 2014. PMID: 24483184 Free PMC article.
-
Treatment with hESC-Derived Myocardial Precursors Improves Cardiac Function after a Myocardial Infarction.PLoS One. 2015 Jul 31;10(7):e0131123. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0131123. eCollection 2015. PLoS One. 2015. PMID: 26230835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Lloyd-Jones D, Adams R, Carnethon M, De Simone G, Ferguson TB, et al. Heart disease and stroke statistics—2009 update: a report from the American Heart Association Statistics Committee and Stroke Statistics Subcommittee. Circulation. 2009;119:480–486. - PubMed
-
- Chien KR, Domian IJ, Parker KK. Cardiogenesis and the complex biology of regenerative cardiovascular medicine. Science. 2008;322:1494–1497. - PubMed
-
- Nussbaum J, Minami E, Laflamme MA, Virag JA, Ware CB, et al. Transplantation of undifferentiated murine embryonic stem cells in the heart: teratoma formation and immune response. FASEB J. 2007;21:1345–1357. - PubMed
-
- Laflamme MA, Chen KY, Naumova AV, Muskheli V, Fugate JA, et al. Cardiomyocytes derived from human embryonic stem cells in pro-survival factors enhance function of infarcted rat hearts. Nat Biotechnol. 2007;25:1015–1024. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

