Molecular Cloning of the Genes Encoding the PR55/Bβ/δ Regulatory Subunits for PP-2A and Analysis of Their Functions in Regulating Development of Goldfish, Carassius auratus
- PMID: 21245947
- PMCID: PMC3020040
- DOI: 10.4137/GRSB.S6065
Molecular Cloning of the Genes Encoding the PR55/Bβ/δ Regulatory Subunits for PP-2A and Analysis of Their Functions in Regulating Development of Goldfish, Carassius auratus
Abstract
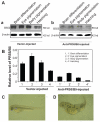
The protein phosphatase-2A (PP-2A), one of the major phosphatases in eukaryotes, is a heterotrimer, consisting of a scaffold A subunit, a catalytic C subunit and a regulatory B subunit. Previous studies have shown that besides regulating specific PP-2A activity, various B subunits encoded by more than 16 different genes, may have other functions. To explore the possible roles of the regulatory subunits of PP-2A in vertebrate development, we have cloned the PR55/B family regulatory subunits: β and δ, analyzed their tissue specific and developmental expression patterns in Goldfish ( Carassius auratus). Our results revealed that the full-length cDNA for PR55/Bβ consists of 1940 bp with an open reading frame of 1332 nucleotides coding for a deduced protein of 443 amino acids. The full length PR55/Bδ cDNA is 2163 bp containing an open reading frame of 1347 nucleotides encoding a deduced protein of 448 amino acids. The two isoforms of PR55/B display high levels of sequence identity with their counterparts in other species. The PR55/Bβ mRNA and protein are detected in brain and heart. In contrast, the PR55/Bδ is expressed in all 9 tissues examined at both mRNA and protein levels. During development of goldfish, the mRNAs for PR55/Bβ and PR55/Bδ show distinct patterns. At the protein level, PR55/Bδ is expressed at all developmental stages examined, suggesting its important role in regulating goldfish development. Expression of the PR55/Bδ anti-sense RNA leads to significant downregulation of PR55/Bδ proteins and caused severe abnormality in goldfish trunk and eye development. Together, our results suggested that PR55/Bδ plays an important role in governing normal trunk and eye formation during goldfish development.
Keywords: PP-2A; PR55/Bβ/δ; developmental regulation; eye; gene expression; lens; phosphorylation; protein phosphatase.
Figures




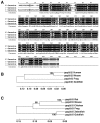
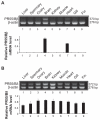
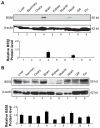
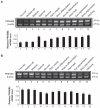

References
-
- Cohen P. The structure and regulation of protein phosphatises. Annu Rev Biochem. 1989;58:453–508. - PubMed
-
- Mumby MC, Walter G. Protein serine/threonine phosphatases: structure, regulation, and functions in cell growth. Physiol Rev. 1993;73:673–99. - PubMed
-
- Hunter T. Protein kinases and phosphatases: the yin and yang of protein phosphorylation and signalling. Cell. 1995;80:225–36. - PubMed
-
- Olsen JV, Blagoev B, Gnad F, et al. Global, in vivo, and site-specific phosphorylation dynamics in signaling networks. Cell. 2006;127:635–48. - PubMed
-
- Moorhead GB, Trinkle-Mulcahy L, Ulke-Lemee A. Emerging roles of nuclear protein phosphatises. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:234–44. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

