Splenic infarction associated with sorafenib use in a hepatocellular carcinoma patient
- PMID: 21246003
- PMCID: PMC3020384
- DOI: 10.3748/wjg.v17.i2.267
Splenic infarction associated with sorafenib use in a hepatocellular carcinoma patient
Abstract
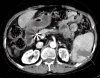
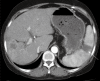
Sorafenib, a multitargeted tyrosine kinase inhibitor, has been shown to improve survival in patients with advanced hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). As the clinical use of sorafenib increases, many adverse effects have been reported, such as hand-foot skin reaction, diarrhea, anorexia, asthenia, alopecia, weight loss, hypertension and arterial thromboembolism. However, there are no prior reports of splenic infarction as an adverse effect of sorafenib. Here, a case of splenic infarction in a patient with HCC who was treated with sorafenib is reported. The patient had no other predisposing factors to explain the splenic infarction except for the administration of sorafenib. The splenic infarction improved after sorafenib was discontinued; however, the HCC progressed.
Keywords: Adverse effects; Hepatocellular carcinoma; Sorafenib; Splenic infarction; Tyrosine kinase inhibitor.
Figures

References
-
- Llovet JM, Ricci S, Mazzaferro V, Hilgard P, Gane E, Blanc JF, de Oliveira AC, Santoro A, Raoul JL, Forner A, et al. Sorafenib in advanced hepatocellular carcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2008;359:378–390. - PubMed
-
- Zangari M, Fink LM, Elice F, Zhan F, Adcock DM, Tricot GJ. Thrombotic events in patients with cancer receiving antiangiogenesis agents. J Clin Oncol. 2009;27:4865–4873. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

