The role of executive function in children's competent adjustment to middle school
- PMID: 21246422
- PMCID: PMC4075458
- DOI: 10.1080/09297049.2010.535654
The role of executive function in children's competent adjustment to middle school
Abstract
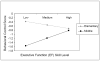
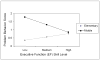
Executive function (EF) skills play an important role in children's cognitive and social functioning. These skills develop throughout childhood, concurrently with a number of developmental transitions and challenges. One of these challenges is the transition from elementary into middle-level schools, which has the potential to significantly disrupt children's academic and social trajectories. However, little is known about the role of EF in children's adjustment during this transition. This study investigated the relation between children's EF skills, assessed both before and during elementary school, and sixth grade academic and social competence. In addition, the influences of the type of school setting attended in sixth grade on children's academic and behavioral outcomes were examined. EF assessed prior to and during elementary school significantly predicted sixth grade competence, as rated by teachers and parents, in both academic and social domains, after controlling for background characteristics. The interactions between type of school setting and EF skills were significant: Parents tended to report more behavioral problems and less regulatory control in children with weaker EF skills who were attending middle school. In contrast, teachers reported greater academic and behavioral difficulty in students with poorer EF attending elementary school settings. In conclusion, children's performance-based EF skills significantly affect adjustment to the academic and behavioral demands of sixth grade, with parent report suggesting greater difficulty for children with poorer EF in settings where children are provided with less external supports (e.g., middle school).
Figures


Similar articles
-
An ecological view of executive function in young children: Variation in and predictors of executive function skills over one school year.Dev Sci. 2023 Jul;26(4):e13355. doi: 10.1111/desc.13355. Epub 2022 Dec 16. Dev Sci. 2023. PMID: 36464793
-
Processes and conditions underlying the link between shyness and school adjustment among Turkish children.Br J Dev Psychol. 2017 Jun;35(2):218-236. doi: 10.1111/bjdp.12158. Epub 2016 Sep 21. Br J Dev Psychol. 2017. PMID: 27653012
-
The development of executive function and language skills in the early school years.J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2016 Feb;57(2):180-7. doi: 10.1111/jcpp.12458. Epub 2015 Aug 26. J Child Psychol Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 26307609 Free PMC article.
-
Parents' Executive Functioning and Involvement in Their Child's Education: An Integrated Literature Review.J Sch Health. 2018 Apr;88(4):322-329. doi: 10.1111/josh.12612. J Sch Health. 2018. PMID: 29498059 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Young Chinese Children's Academic Skill Development: Identifying Child-, Family-, and School-Level Factors.New Dir Child Adolesc Dev. 2019 Jan;2019(163):9-37. doi: 10.1002/cad.20271. Epub 2019 Jan 7. New Dir Child Adolesc Dev. 2019. PMID: 30615267 Review.
Cited by
-
Improved quality of life among adolescents with attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder is mediated by protective factors: a cross sectional survey.BMC Psychiatry. 2015 May 7;15:108. doi: 10.1186/s12888-015-0491-0. BMC Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 25948117 Free PMC article.
-
Parental Warmth and Hostility and Child Executive Function Problems: A Longitudinal Study of Chinese Families.Front Psychol. 2018 Jul 4;9:1063. doi: 10.3389/fpsyg.2018.01063. eCollection 2018. Front Psychol. 2018. PMID: 30022960 Free PMC article.
-
Executive function is associated with social competence in preschool-aged children born preterm or full term.Early Hum Dev. 2014 Jun;90(6):299-306. doi: 10.1016/j.earlhumdev.2014.02.011. Epub 2014 Mar 21. Early Hum Dev. 2014. PMID: 24661446 Free PMC article.
-
The effectiveness of a tablet-based video game that stimulates cognitive, emotional, and social skills in developing academic skills among preschoolers: study protocol for a randomized controlled trial.Trials. 2022 Nov 9;23(1):936. doi: 10.1186/s13063-022-06875-9. Trials. 2022. PMID: 36352445 Free PMC article.
-
Prenatal organophosphorus pesticide exposure and executive function in preschool-aged children in the Norwegian Mother, Father and Child Cohort Study (MoBa).Environ Res. 2022 Sep;212(Pt D):113555. doi: 10.1016/j.envres.2022.113555. Epub 2022 May 22. Environ Res. 2022. PMID: 35613628 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Achenbach TM. Manual for the Teacher’s Report Form and 1991 Profile. Burlington, VT: University of Vermont, Department of Psychiatry; 1991.
-
- Akos P, Queen JA, Lineberry C. Promoting a successful transition to middle school. Larchmont, New York: Eye on Education; 2005.
-
- Alspaugh JW. Achievement loss associated with the transition to middle school and high school. Journal of Educational Research. 1998;92:20–26.
-
- Anderman EM. The middle school experience: Effects on the math and science achievement of adolescents with LD. Journal of Learning Disabilities. 1998;31:128–138. - PubMed
-
- Anderson P. Assessment and development of executive function (EF) during childhood. Child Neuropsychology. 2002;8:71–82. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
