Characterization of combinatorial patterns generated by multiple two-component sensors in E. coli that respond to many stimuli
- PMID: 21246512
- PMCID: PMC3413328
- DOI: 10.1002/bit.22966
Characterization of combinatorial patterns generated by multiple two-component sensors in E. coli that respond to many stimuli
Abstract
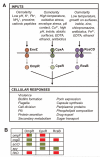
Two-component systems enable bacteria to sense changes in their environment and adjust gene expression in response. Multiple two-component systems could function as a combinatorial sensor to discriminate environmental conditions. A combinatorial sensor is composed of a set of sensors that are non-specifically activated to different magnitudes by many stimuli, such that their collective activity pattern defines the signal. Using promoter reporters and flow cytometry, we measured the response of three two-component systems in Escherichia coli that have been previously reported to respond to many environmental stimuli (EnvZ/OmpR, CpxA/CpxR, and RcsC/RcsD/RcsB). A chemical library was screened for the ability to activate the sensors and 13 inducers were identified that produce different patterns of sensor activity. The activities of the three systems are uncorrelated with each other and the osmolarity of the inducing media. Five of the seven possible non-trivial patterns generated by three sensors are observed. This data demonstrate one mechanism by which bacteria are able to use a limited set of sensors to identify a diverse set of compounds and environmental conditions.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley Periodicals, Inc.
Figures




References
-
- Ache BW, Young JM. Olfaction: Diverse species, conserved principles. Neuron. 2005;48(3):417–430. - PubMed
-
- Aiba H, Mizuno T, Mizushima S. Transfer of phosphoryl group between two regulatory proteins involved in osmoregulatory expression of the ompF and ompC genes in Escherichia coli. J Biol Chem. 1989;264(15):8563–8567. - PubMed
-
- Anderson JC, Clarke EJ, Arkin AP, Voigt CA. Environmentally controlled invasion of cancer cells by engineered bacteria. J Mol Biol. 2006;355(4):619–627. - PubMed
-
- Arricau N, Hermant D, Waxin H, Ecobichon C, Duffey PS, Popoff MY. The RcsB–RcsC regulatory system of Salmonella typhi differentially modulates the expression of invasion proteins, flagellin and Vi antigen in response to osmolarity. Mol Microbiol. 2002;29:835–850. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

