Effect of B-cell depletion on coreceptor switching in R5 simian-human immunodeficiency virus infection of rhesus macaques
- PMID: 21248033
- PMCID: PMC3067891
- DOI: 10.1128/JVI.02150-10
Effect of B-cell depletion on coreceptor switching in R5 simian-human immunodeficiency virus infection of rhesus macaques
Abstract
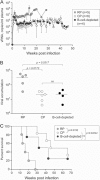
We recently described a coreceptor switch in rapid progressor (RP) R5 simian-human immunodeficiency virus SF162P3N (SHIV(SF162P3N))-infected rhesus macaques that had high virus replication and undetectable or weak and transient antiviral antibody response (S. H. Ho et al., J. Virol. 81:8621-8633, 2007; S. H. Ho, N. Trunova, A. Gettie, J. Blanchard, and C. Cheng-Mayer, J. Virol. 82:5653-5656, 2008; and W. Ren et al., J. Virol. 84:340-351, 2010). The lack of antibody selective pressure, together with the observation that the emerging X4 variants were neutralization sensitive, suggested that the absence or weakening of the virus-specific humoral immune response could be an environmental factor fostering coreceptor switching in vivo. To test this possibility, we treated four macaques with 50 mg/kg of body weight of the anti-CD20 antibody rituximab every 2 to 3 weeks starting from the week prior to intravenous infection with SHIV(SF162P3N) for a total of six infusions. Rituximab treatment successfully depleted peripheral and lymphoid CD20(+) cells for up to 25 weeks according to flow cytometry and immunohistochemical staining, with partial to full recovery in two of the four treated monkeys thereafter. Three of the four treated macaques failed to mount a detectable anti-SHIV antibody response, while the response was delayed in the remaining animal. The three seronegative macaques progressed to disease, but in none of them could the presence of X4 variants be demonstrated by V3 sequence and tropism analyses. Furthermore, viruses did not evolve early in these diseased macaques to be more soluble CD4 sensitive. These results demonstrate that the absence or diminution of humoral immune responses by itself is insufficient to drive the R5-to-X4 switch and the neutralization susceptibility of the evolving viruses.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Identification of interdependent variables that influence coreceptor switch in R5 SHIV(SF162P3N)-infected macaques.Retrovirology. 2012 Dec 13;9:106. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-9-106. Retrovirology. 2012. PMID: 23237529 Free PMC article.
-
V3 loop-determined coreceptor preference dictates the dynamics of CD4+-T-cell loss in simian-human immunodeficiency virus-infected macaques.J Virol. 2005 Oct;79(19):12296-303. doi: 10.1128/JVI.79.19.12296-12303.2005. J Virol. 2005. PMID: 16160156 Free PMC article.
-
Different tempo and anatomic location of dual-tropic and X4 virus emergence in a model of R5 simian-human immunodeficiency virus infection.J Virol. 2010 Jan;84(1):340-51. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01865-09. J Virol. 2010. PMID: 19846515 Free PMC article.
-
Novel Strategy To Adapt Simian-Human Immunodeficiency Virus E1 Carrying env from an RV144 Volunteer to Rhesus Macaques: Coreceptor Switch and Final Recovery of a Pathogenic Virus with Exclusive R5 Tropism.J Virol. 2018 Jun 29;92(14):e02222-17. doi: 10.1128/JVI.02222-17. Print 2018 Jul 15. J Virol. 2018. PMID: 29743361 Free PMC article.
-
Coreceptor switch in infection of nonhuman primates.Curr HIV Res. 2009 Jan;7(1):30-8. doi: 10.2174/157016209787048500. Curr HIV Res. 2009. PMID: 19149552 Review.
Cited by
-
Anti-viral efficacy of a next-generation CD4-binding site bNAb in SHIV-infected animals in the absence of anti-drug antibody responses.iScience. 2022 Sep 5;25(10):105067. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.105067. eCollection 2022 Oct 21. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36157588 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of interdependent variables that influence coreceptor switch in R5 SHIV(SF162P3N)-infected macaques.Retrovirology. 2012 Dec 13;9:106. doi: 10.1186/1742-4690-9-106. Retrovirology. 2012. PMID: 23237529 Free PMC article.
-
Evolution of HIV-1 coreceptor usage and coreceptor switching during pregnancy.AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2014 Mar;30(3):312-24. doi: 10.1089/aid.2013.0155. Epub 2013 Oct 25. AIDS Res Hum Retroviruses. 2014. PMID: 24090041 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of B Cell Depletion on Early Mycobacterium tuberculosis Infection in Cynomolgus Macaques.Infect Immun. 2016 Apr 22;84(5):1301-1311. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00083-16. Print 2016 May. Infect Immun. 2016. PMID: 26883591 Free PMC article.
-
Non-neutralizing Antibodies May Contribute to Suppression of SIVmac239 Viremia in Indian Rhesus Macaques.Front Immunol. 2021 Mar 16;12:657424. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.657424. eCollection 2021. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33796119 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ahuja, A., et al. 2007. Depletion of B cells in murine lupus: efficacy and resistance. J. Immunol. 179:3351-3361. - PubMed
-
- Appay, V., D. C. Douek, and D. A. Price. 2008. CD8+ T-cell efficacy in vaccination and disease. Nat. Med. 14:623-628. - PubMed
-
- Berger, E. A., P. M. Murphy, and J. M. Farber. 1999. Chemokine receptors as HIV-1 coreceptors: roles in viral entry, tropism, and disease. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 17:657-700. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

