Visualization and identification of the structures formed during early stages of fibrin polymerization
- PMID: 21248064
- PMCID: PMC3099577
- DOI: 10.1182/blood-2010-07-297671
Visualization and identification of the structures formed during early stages of fibrin polymerization
Abstract
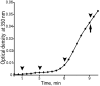
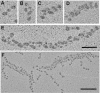
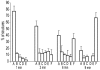
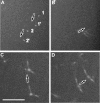
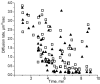
We determined the sequence of events and identified and quantitatively characterized the mobility of moving structures present during the early stages of fibrin-clot formation from the beginning of polymerization to the gel point. Three complementary techniques were used in parallel: spinning-disk confocal microscopy, transmission electron microscopy, and turbidity measurements. At the beginning of polymerization the major structures were monomers, whereas at the middle of the lag period there were monomers, oligomers, protofibrils (defined as structures that consisted of more than 8 monomers), and fibers. At the end of the lag period, there were primarily monomers and fibers, giving way to mainly fibers at the gel point. Diffusion rates were calculated from 2 different results, one based on sizes and another on the velocity of the observed structures, with similar results in the range of 3.8-0.1 μm²/s. At the gel point, the diffusion coefficients corresponded to very large, slow-moving structures and individual protofibrils. The smallest moving structures visible by confocal microscopy during fibrin polymerization were identified as protofibrils with a length of approximately 0.5 μm. The sequence of early events of clotting and the structures present are important for understanding hemostasis and thrombosis.
Figures
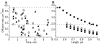
Comment in
-
To gel or not to gel.Blood. 2011 Apr 28;117(17):4406-7. doi: 10.1182/blood-2011-02-332767. Blood. 2011. PMID: 21527539 No abstract available.
References
-
- Doolittle RF. Fibrinogen and fibrin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:195–229. - PubMed
-
- Cierniewski CS, Kloczewiak M, Budzynski AZ. Expression of primary polymerization sites in the D domain of human fibrinogen depends on intact conformation. J Biol Chem. 1986;261(20):9116–9121. - PubMed
-
- Fowler WE, Erickson HP, Hantgan RR, McDonagh J, Hermans J. Cross-linked fibrinogen dimers demonstrate a feature of the molecular packing in fibrin fibers. Science. 1981;211(4479):287–289. - PubMed
-
- Weisel JW, Phillips GN, Jr., Cohen C. A model from electron microscopy for the molecular structure of fibrinogen and fibrin. Nature. 1981;289(5795):263–267. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

