The suppressive effect of an intra-prefrontal cortical infusion of BDNF on cocaine-seeking is Trk receptor and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase dependent
- PMID: 21248106
- PMCID: PMC4360979
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4986-10.2011
The suppressive effect of an intra-prefrontal cortical infusion of BDNF on cocaine-seeking is Trk receptor and extracellular signal-regulated protein kinase mitogen-activated protein kinase dependent
Abstract
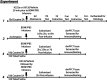
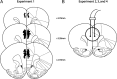
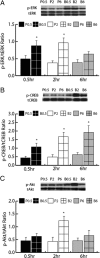
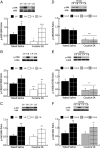
Cocaine-mediated neuroadaptations in the prefrontal cortical-nucleus accumbens pathway underlie drug-seeking in animals with a cocaine self-administration (SA) history. Neuroplasticity in the cortico-accumbens pathway is regulated, in part, by the expression and availability of neurotrophic factors, such as BDNF. We have previously demonstrated that infusion of BDNF into the dorsomedial prefrontal cortex (dmPFC) immediately after the last of 10 cocaine SA sessions attenuates contextual, cue- and cocaine prime-induced reinstatement of cocaine-seeking (Berglind et al., 2007) and normalizes cocaine-induced disruption of glutamatergic transmission in the nucleus accumbens (Berglind et al., 2009). In the present study, the suppressive effect of intra-dmPFC BDNF on cocaine-seeking is shown to depend on Trk receptor-mediated activation of extracellular signal-regulated kinase (ERK) signaling in the dmPFC. The tyrosine kinase inhibitor, K252a, and the mitogen-activated protein/extracellular signal-regulated kinase kinase inhibitor, U0126 (1,4-diamino-2,3-dicyano-1,4-bis[2-aminophenylthio]butadiene), prevented BDNF's suppressive effects on cocaine-seeking. Vehicle-infused rats with a cocaine SA history showed significant decreases in ERK and cyclic AMP response element binding protein (CREB), but not Akt, phosphorylation after the final cocaine SA session that were reversed by intra-dmPFC BDNF. Additionally, BDNF's ability to normalize cocaine-mediated decreases in ERK and CREB phosphorylation was blocked by U0126, demonstrating that ERK/MAPK activation mediated the behavioral effects. This study elucidates a mechanism whereby BDNF/TrkB (tropomyosin receptor kinase B) activates ERK-regulated CREB phosphorylation in the dmPFC to counteract the neuroadaptations induced by cocaine SA and subsequent relapse to cocaine-seeking.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Role of Src Family Kinases in BDNF-Mediated Suppression of Cocaine-Seeking and Prevention of Cocaine-Induced ERK, GluN2A, and GluN2B Dephosphorylation in the Prelimbic Cortex.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017 Sep;42(10):1972-1980. doi: 10.1038/npp.2017.114. Epub 2017 Jun 6. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2017. PMID: 28585567 Free PMC article.
-
Relapse to cocaine-seeking after abstinence is regulated by cAMP-dependent protein kinase A in the prefrontal cortex.Addict Biol. 2014 Jan;19(1):77-86. doi: 10.1111/adb.12043. Epub 2013 Mar 6. Addict Biol. 2014. PMID: 23461423 Free PMC article.
-
Divergent Prelimbic Cortical Pathways Interact with BDNF to Regulate Cocaine-seeking.J Neurosci. 2018 Oct 17;38(42):8956-8966. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1332-18.2018. Epub 2018 Sep 5. J Neurosci. 2018. PMID: 30185459 Free PMC article.
-
Brain-derived neurotrophic factor and cocaine addiction.Brain Res. 2010 Feb 16;1314:183-93. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2009.08.078. Epub 2009 Sep 2. Brain Res. 2010. PMID: 19732758 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cocaine self-administration causes signaling deficits in corticostriatal circuitry that are reversed by BDNF in early withdrawal.Brain Res. 2015 Dec 2;1628(Pt A):82-7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2014.09.050. Epub 2014 Sep 28. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25268928 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The effects of cocaine exposure in adolescence: Behavioural effects and neuroplastic mechanisms in experimental models.Br J Pharmacol. 2022 Sep;179(17):4233-4253. doi: 10.1111/bph.15523. Epub 2021 Jun 8. Br J Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 33963539 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Overexpression of neuronal RNA-binding protein HuD increases reward induced reinstatement of an instrumental response.Neurosci Lett. 2018 Sep 14;683:119-124. doi: 10.1016/j.neulet.2018.06.038. Epub 2018 Jun 22. Neurosci Lett. 2018. PMID: 29940328 Free PMC article.
-
Corticostriatal BDNF and alcohol addiction.Brain Res. 2015 Dec 2;1628(Pt A):60-7. doi: 10.1016/j.brainres.2015.03.025. Epub 2015 Mar 21. Brain Res. 2015. PMID: 25801118 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Systemic Delivery of a Brain-Penetrant TrkB Antagonist Reduces Cocaine Self-Administration and Normalizes TrkB Signaling in the Nucleus Accumbens and Prefrontal Cortex.J Neurosci. 2016 Aug 3;36(31):8149-59. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2711-14.2016. J Neurosci. 2016. PMID: 27488635 Free PMC article.
-
Psychedelic-inspired approaches for treating neurodegenerative disorders.J Neurochem. 2022 Jul;162(1):109-127. doi: 10.1111/jnc.15544. Epub 2021 Dec 5. J Neurochem. 2022. PMID: 34816433 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berglind WJ, See RE, Fuchs RA, Ghee SM, Whitfield TW, Jr, Miller SW, McGinty JF. A BDNF infusion into the medial prefrontal cortex suppresses cocaine seeking in rats. Eur J Neurosci. 2007;26:757–766. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
