Hyaluronan as an immune regulator in human diseases
- PMID: 21248167
- PMCID: PMC3051404
- DOI: 10.1152/physrev.00052.2009
Hyaluronan as an immune regulator in human diseases
Abstract
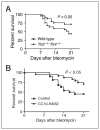
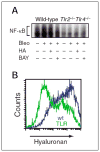
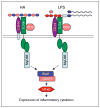
Accumulation and turnover of extracellular matrix components are the hallmarks of tissue injury. Fragmented hyaluronan stimulates the expression of inflammatory genes by a variety of immune cells at the injury site. Hyaluronan binds to a number of cell surface proteins on various cell types. Hyaluronan fragments signal through both Toll-like receptor (TLR) 4 and TLR2 as well as CD44 to stimulate inflammatory genes in inflammatory cells. Hyaluronan is also present on the cell surface of epithelial cells and provides protection against tissue damage from the environment by interacting with TLR2 and TLR4. Hyaluronan and hyaluronan-binding proteins regulate inflammation, tissue injury, and repair through regulating inflammatory cell recruitment, release of inflammatory cytokines, and cell migration. This review focuses on the role of hyaluronan as an immune regulator in human diseases.
Figures




References
-
- Acharya PS, Majumdar S, Jacob M, Hayden J, Mrass P, Weninger W, Assoian RK, Pure E. Fibroblast migration is mediated by CD44-dependent TGF beta activation. J Cell Sci. 2008;121:1393–1402. - PubMed
-
- Aderem A, Ulevitch RJ. Toll-like receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature. 2000;406:782–787. - PubMed
-
- Agren UM, Tammi RH, Tammi MI. Reactive oxygen species contribute to epidermal hyaluronan catabolism in human skin organ culture. Free Radic Biol Med. 1997;23:996–1001. - PubMed
-
- Akishima Y, Ito K, Zhang L, Ishikawa Y, Orikasa H, Kiguchi H, Akasaka Y, Komiyama K, Ishii T. Immunohistochemical detection of human small lymphatic vessels under normal and pathological conditions using the LYVE-1 antibody. Virchows Arch. 2004;444:153–157. - PubMed
-
- Al Qteishat A, Gaffney JJ, Krupinski J, Slevin M. Hyaluronan expression following middle cerebral artery occlusion in the rat. Neuroreport. 2006;17:1111–1114. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

