Rebiopsy of lung cancer patients with acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors and enhanced detection of the T790M mutation using a locked nucleic acid-based assay
- PMID: 21248300
- PMCID: PMC3070951
- DOI: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-2277
Rebiopsy of lung cancer patients with acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors and enhanced detection of the T790M mutation using a locked nucleic acid-based assay
Abstract
Background: The epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) mutation T790M is reported in approximately 50% of lung cancers with acquired resistance to EGFR inhibitors and is a potential prognostic and predictive biomarker. Its assessment can be challenging due to limited tissue availability and underdetection at low mutant allele levels. Here, we sought to determine the feasibility of tumor rebiopsy and to more accurately assess the prevalence of the T790M using a highly sensitive locked nucleic acid (LNA) PCR/sequencing assay. MET amplification was also analyzed.
Methods: Patients with acquired resistance were rebiopsied and samples were studied for sensitizing EGFR mutations. Positive cases were evaluated for T790M using standard PCR-based methods and a subset were re-evaluated with an LNA-PCR/sequencing method with an analytical sensitivity of approximately 0.1%. MET amplification was assessed by FISH.
Results: Of 121 patients undergoing tissue sampling, 104 (86%) were successfully analyzed for sensitizing EGFR mutations. Most failures were related to low tumor content. All patients (61/61) with matched pretreatment and resistance specimens showed concordance for the original sensitizing EGFR mutation. Standard T790M mutation analysis on 99 patients detected 51(51%) mutants. Retesting of 30 negative patients by the LNA-based method detected 11 additional mutants for an estimated prevalence of 68%. MET was amplified in 11% of cases (4/37).
Conclusions: The re-biopsy of lung cancer patients with acquired resistance is feasible and provides sufficient material for mutation analysis in most patients. Using high sensitivity methods, the T790M is detected in up to 68% of these patients.
©2011 AACR.
Figures


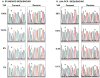
 ) denotes SNP at position 2361. B. LNA-PCR/sequencing. With the introduction of the LNA probe, only the mutant peak (T) is seen at position 2369 (arrow) at all dilutions of 0.8% and above. At progressively lower concentrations, the WT peak becomes visible but the mutant peak remains predominant down to 0.1% (percentages have been rounded). At the SNP position (
) denotes SNP at position 2361. B. LNA-PCR/sequencing. With the introduction of the LNA probe, only the mutant peak (T) is seen at position 2369 (arrow) at all dilutions of 0.8% and above. At progressively lower concentrations, the WT peak becomes visible but the mutant peak remains predominant down to 0.1% (percentages have been rounded). At the SNP position ( ) only G is seen with complete suppression of the WT allele.
) only G is seen with complete suppression of the WT allele.References
-
- Ladanyi M, Pao W. Lung adenocarcinoma: guiding EGFR-targeted therapy and beyond. Mod Pathol. 2008;21 (Suppl 2):S16–22. - PubMed
-
- Lynch TJ, Bell DW, Sordella R, et al. Activating mutations in the epidermal growth factor receptor underlying responsiveness of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N Engl J Med. 2004;350:2129–39. - PubMed
-
- Paez JG, Janne PA, Lee JC, et al. EGFR mutations in lung cancer: correlation with clinical response to gefitinib therapy. Science. 2004;304:1497–500. - PubMed
-
- Mok TS, Wu YL, Thongprasert S, et al. Gefitinib or carboplatin-paclitaxel in pulmonary adenocarcinoma. N Engl J Med. 2009;361:947–57. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

