Phospholipases in action during plant defense signaling
- PMID: 21248491
- PMCID: PMC3121997
- DOI: 10.4161/psb.6.1.14037
Phospholipases in action during plant defense signaling
Abstract
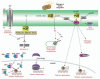
Eukaryotic organisms rely on intricate signaling networks to connect recognition of microbes with the activation of efficient defense reactions. Accumulating evidence indicates that phospholipids are more than mere structural components of biological membranes. Indeed, phospholipid-based signal transduction is widely used in plant cells to relay perception of extracellular signals. Upon perception of the invading microbe, several phospholipid hydrolyzing enzymes are activated that contribute to the establishment of an appropriate defense response. Activation of phospholipases is at the origin of the production of important defense signaling molecules, such as oxylipins and jasmonates, as well as the potent second messenger phosphatidic acid (PA), which has been shown to modulate the activity of a variety of proteins involved in defense signaling. Here, we provide an overview of recent reports describing the different plant phospholipase pathways that are activated during the establishment of plant defense reactions in response to pathogen attack.
Figures

References
-
- Zipfel C. Pattern-recognition receptors in plant innate immunity. Curr Opin Immunol. 2008;20:10–16. - PubMed
-
- Jones JD, Dangl JL. The plant immune system. Nature. 2006;444:323–329. - PubMed
-
- Rivas S, Thomas CM. Molecular interactions between tomato and the leaf mold pathogen Cladosporium fulvum. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2005;43:395–436. - PubMed
-
- Boller T, Felix G. A renaissance of elicitors: perception of microbe-associated molecular patterns and danger signals by pattern-recognition receptors. Annu Rev Plant Biol. 2009;60:379–406. - PubMed
-
- Shah J. Lipids, lipases and lipid-modifying enzymes in plant disease resistance. Annu Rev Phytopathol. 2005;43:229–260. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
