Analgesia in patients with acute abdominal pain
- PMID: 21249672
- PMCID: PMC12296243
- DOI: 10.1002/14651858.CD005660.pub3
Analgesia in patients with acute abdominal pain
Abstract
Background: For decades, the indication of analgesia in patients with Acute Abdominal Pain (AAP) has been deferred until the definitive diagnosis has been made, for fear of masking symptoms, generating a change in the physical exploration or obstructing the diagnosis of a disease requiring surgical treatment. This strategy has been questioned by some studies that have shown that the use of analgesia in the initial evaluation of patients with AAP leads to a significant reduction in pain without affecting diagnostic accuracy.
Objectives: To determine whether the evidence available supports the use of opioid analgesics in the diagnostic process of patients with AAP.
Search strategy: Trials were identified through searches in Cochrane Controlled Trials Register (CENTRAL) (The Cochrane Library, issue 2, 2009), MEDLINE (1966 to 2009) and EMBASE (1980 to 2009). A randomised controlled trial (RCT) filter for a MEDLINE search was applied (with appropriate modification for an EMBASE search). Trials also were identified through "related articles". The search was not limited by language or publication status.
Selection criteria: All published RCTs which included adult patients with AAP, without gender restriction, comparing any opioids analgesia regimen with the non-use of analgesic before any intervention and independent of the results.
Data collection and analysis: Two independent reviewers assessed the studies identified via the electronic search. Articles that were relevant and pertinent to the aims of the study were selected and their respective full-text versions were collected for subsequent blinded evaluation. The allocation concealment was considered in particular as an option to diminish the biases.The data collected from the studies were reviewed qualitatively and quantitatively using the Cochrane Collaboration statistical software RevMan 5.0. After performing the meta-analysis, the chi-squared test for heterogeneity was applied. In situations of significant clinical heterogeneity, statistical analyses were not applied to the pool of results. In situations of heterogeneity, the random effect model was used to perform the meta-analysis of the results. A sensitivity analysis was also applied based on the evaluation to the methodological quality of the primary studies.
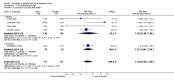
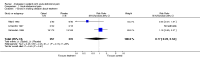
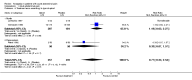
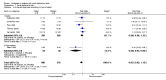
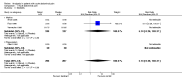
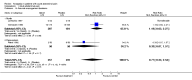
Main results: Eight studies fulfilled the inclusion criteria. Differences with use of opioid analgesia were verified in variables: Change in the intensity of the pain, change in the patients comfort level.
Authors' conclusions: The use of opioid analgesics in the therapeutic diagnosis of patients with AAP does not increase the risk of diagnosis error or the risk of error in making decisions regarding treatment.
Conflict of interest statement
None Known.
Figures







Update of
-
Analgesia in patients with acute abdominal pain.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007 Jul 18;(3):CD005660. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005660.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2007. Update in: Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2011 Jan 19;(1):CD005660. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD005660.pub3. PMID: 17636812 Updated.
References
References to studies included in this review
Amoli 2008 {published data only}
-
- Amoli HA, Golozar A, Keshavarzi S, Tavakoli H, Yaghoobi A. Morphine analgesia in patients with acute appendicitis: A randomised double‐blind clinical trial.. Emergency Medicine Journal 2008;25(9):586‐589. - PubMed
Attard 1992 {published data only}
Gallagher 2006 {published data only}
-
- Gallagher EJ, Esses D, Lee C, Lahn M, Bijur PE. Randomized clinical trial of morphine in acute abdominal pain.. Ann Emerg Med 2006;48(2):150‐160.. - PubMed
LoVecchio 1997 {published data only}
-
- LoVecchio F, Oster N, Sturmann K, Nelson LS, Flashner S, Finger R. The use of analgesics in patients with acute abdominal pain. J Emerg Med 1997;15(6):775‐779. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mahadevan 2000 {published data only}
-
- Mahadevan M, Graff L. Prospective randomized study of analgesic use for ED patients with right lower quadrant abdominal pain. Am J Emerg Med 2000;18(7):753‐756. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Pace 1996 {published data only}
-
- Pace S, Burke TF. Intravenous morphine for early pain relief in patients with acute abdominal pain. Acad Emerg Med 1996;3(12):1086‐1092. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Thomas 2003a {published data only}
-
- Thomas SH, Silen W, Cheema F, Reisner A, Aman S, Goldstein JN, Kumar AM, Stair TO. Effects of morphine analgesia on diagnostic accuracy in Emergency Department patients with abdominal pain: a prospective, randomized trial. J Am Coll Surg 2003;196(1):18‐31. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vermeulen 1999 {published data only}
-
- Vermeulen B, Morabia A, Unger PF, Goehring C, Grangier C, Skljarov I, Terrier F. Acute appendicitis: influence of early pain relief on the accuracy of clinical and US findings in the decision to operate‐‐a randomized trial. Radiology 1999;210(3):639‐643. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
References to studies excluded from this review
Al‐Waili 1998 {published data only}
-
- Al‐Waili N, Saloom KY. The analgesic effect of intravenous tenoxicam in symptomatic treatment of biliary colic: a comparison with hyoscine N‐butylbromide. Eur J Med Res 1998;3(10):475‐479. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Alshehri 1995 {published data only}
-
- Alshehri MY, Ibrahim A, Abuaisha N, Malatani T, Abu‐Eshy S, Khairulla S, Bahamdan K. Value of rebound tenderness in acute appendicitis. East Afr Med J 1995;72(8):504‐506. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Anderson 2000 {published data only}
-
- Andersson RE, Hugander AP, Ghazi SH, Ravn H, Offenbartl SK, Nystrom PO, Olaison GP. Why does the clinical diagnosis fail in suspected appendicitis?. Eur J Surg 2000;166(10):796‐802. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Bailey 2007 {published data only}
-
- Bailey B, Bergeron S, Gravel J, Bussieres JF, Bensoussan A. Efficacy and Impact of Intravenous Morphine Before Surgical Consultation in Children With Right Lower Quadrant Pain Suggestive of Appendicitis: A Randomized Controlled Trial.. Annals of Emergency Medicine 2007;50(4):371‐378. - PubMed
Cardall 2004 {published data only}
-
- Cardall T, Glasser J, Guss DA. Clinical value of the total white blood cell count and temperature in the evaluation of patients with suspected appendicitis. Acad Emerg Med 2004;11(10):1021‐1027. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Champault 1993 {published data only}
-
- Champault G, Rizk N, Lauroy J, Olivares P, Belhassen A, Boutelier P. Right iliac fossa pain in women. Conventional diagnostic approach versus primary laparoscopy. A controlled study (65 cases). Ann Chir 1993;47(4):316‐319. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chaudhary 1999 {published data only}
-
- Chaudhary A, Gupta RL. Double blind, randomised, parallel, prospective, comparative, clinical evaluation of a combination of antispasmodic analgesic Diclofenac + Pitofenone + Fenpiverinium (Manyana) vs Analgin + Pitofenone + Fenpiverinium (Baralgan) in biliary, ureteric and intestinal colic. J Indian Med Assoc 1999;97(2):72‐75. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Chong 2004 {published data only}
Clarke 1991 {published data only}
-
- Clarke JR, Badawy SB. Acute pain over the appendix. A model of the surgical decision. Ann Chir 1991;45(4):279‐283. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Clère 2002 {published data only}
-
- Clère F, Soriot‐Thomas S. Acute abdominal pain... should be relieved rapidly! [La douleur adbominale aiguë: un mal à combattre .... rapidement !]. Presse Med. 2002 Sep 14;31(29):1348‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
de los Santos 1999 {published data only}
-
- Santos AR, Marti ML, Girolamo G, Diego Espinosa J, Morano MA, Tobar JC, Prete C. Propinox in biliary colic: a multicenter, randomized, prospective and parallel double‐blind study of three doses of propinox versus placebo in acute biliary colic pain. Int J Tissue React 1999;21(1):13‐18. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Decadt 1999 {published data only}
-
- Decadt B, Sussman L, Lewis MP, Secker A, Cohen L, Rogers C, Patel A, Rhodes M. Randomized clinical trial of early laparoscopy in the management of acute non‐specific abdominal pain. Br J Surg 1999;86(11):1383‐1386. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Eskelinen 1995 {published data only}
-
- Eskelinen M, Ikonen J, Lipponen P. The value of history‐taking, physical examination, and computer assistance in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in patients more than 50 years old. Scand J Gastroenterol 1995;30(4):349‐355. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Franke 2002 {published data only}
-
- Franke C, Gerharz CD, Bohner H, Ohmann C, Heydrich G, Kramling HJ, Stock W, Rosen D, Kurpreugsch K, Roher HD. Neurogenic appendicopathy: a clinical disease entity?. Int J Colorectal Dis 2002;17(3):185‐191. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Frei 2008 {published data only}
-
- Frei SP, Bond WF, Bazuro RK, Richardson DM, Sierzega GM, Wasser TE. Is early analgesia associated with delayed treatment of appendicitis?. American Journal of Emergency Medicine 2008;26(2):176‐180. - PubMed
Furyk 2008 {published data only}
-
- Furyk J, Sumner M. Pain score documentation and analgesia: A comparison of children and adults with appendicitis.. Emergency Medicine Australasia 2008;20(6):482‐487. - PubMed
Gaitan 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gaitan H, Angel E, Sanchez J, Gomez I, Sanchez L, Agudelo C. Laparoscopic diagnosis of acute lower abdominal pain in women of reproductive age. Int J Gynaecol Obstet 2002;76(2):149‐158. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Gallagher 2002 {published data only}
-
- Gallagher EJ, Bijur PE, Latimer C, Silver W. Reliability and validity of a visual analog scale for acute abdominal pain in the ED. Am J Emerg Med 2002;20(4):287‐290. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Garyfallou 1997 {published and unpublished data}
-
- Garyfallou GT, Grillo A, O’Connor RE, Fulda GJ, Levine BJ. A controlled trial of fentanyl analgesia in emergency department patients with abdominal pain:can treatment obscure the diagnosis? [abstract]. Acad Emerg Med 1997;4:424.
Graff 2000 {published data only}
-
- Graff L, Russell J, Seashore J, Tate J, Elwell A, Prete M, Werdmann M, Maag R, Krivenko C, Radford M. False‐negative and false‐positive errors in abdominal pain evaluation: failure to diagnose acute appendicitis and unnecessary surgery. Acad Emerg Med 2000;7(11):1244‐1255. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Green 2005 {published data only}
-
- Green R, Bulloch B, Kabani A. Early analgesia for children with acute abdominal pain.. Pediatrics 2005;116:978‐983.. - PubMed
Hong 2003 {published data only}
-
- Hong JJ, Cohn SM, Ekeh AP, Newman M, Salama M, Leblang SD. Miami Appendicitis Group. A prospective randomized study of clinical assessment versus computed tomography for the diagnosis of acute appendicitis. Surg Infect (Larchmt) 2003;4(3):231‐239. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kim 2002 {published data only}
-
- Kim MK, Strait RT, Sato TT, Hennes HM. A randomized clinical trial of analgesia in children with acute abdominal pain. Acad Emerg Med 2002;9(4):281‐287. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Kokki 2005 {published data only}
-
- Kokki H, Lintula H, Vanamo K, Heiskanen M, Eskelinen M. Oxycodone versus placebo inchildren with undifferentiated abdominal pain.. Arch Pediat Adolesc Med 2005;159:320‐325. - PubMed
Lane 1997 {published data only}
Lee 2000 {published data only}
-
- Lee JS, Stiell IG, Wells GA, Elder BR, Vandemheen K, Shapiro S. Adverse outcomes and opioid analgesic administration in acute abdominal pain. Acad Emerg Med 2000;7(9):980‐987. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Marinsek 2007 {published data only}
-
- Marinsek M, Kovacic D, Versnik D, Parasuh M, Golez S, Podbregar M. Analgesic treatment and predictors of satisfaction with analgesia in patients with acute undifferentiated abdominal pain. European Journal of Pain 2007;11(7):773‐778.. - PubMed
McHale 2001 {published data only}
-
- McHale PM, LoVecchio F. Narcotic analgesia in the acute abdomen‐‐a review of prospective trials. Eur J Emerg Med 2001;8(2):131‐136. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Milojevic 2001 {published data only}
-
- Milojevic K, Cantineau JP, Simon L, Bataille S, Ruiz R, Coudert B, Simon N, Lambert Y, Groupe Dassy. Acute severe pain in emergencies. The key for efficient analgesia. Ann Fr Anesth Reanim 2001;20(9):745‐751. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mittal 2004 {published data only}
-
- Mittal VK, Goliath J, Sabir M, Patel R, Richards BF, Alkalay I, ReMine S, Edwards M. Advantages of focused helical computed tomographic scanning with rectal contrast only vs triple contrast in the diagnosis of clinically uncertain acute appendicitis: a prospective randomized study. Arch Surg 2004;139(5):495‐499. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ng 2002 {published data only}
Niederau 1999 {published data only}
-
- Niederau C, Gopfert E. The effect of chelidonium‐ and turmeric root extract on upper abdominal pain due to functional disorders of the biliary system. Results from a placebo‐controlled double‐blind study. Med Klin (Munich) 1999;94(8):425‐430. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Nik Hisamuddin 2008 {published data only}
-
- Nik Hisamuddin NAR, Kamaruddin J, Idzwan ZM, Rashidi A. Comparison of acute pain relief, after intravenous morphine administration, among different ethnic groups who presented with acute abdominal pain in the Emergency Department.. Journal of Emergency Medicine, Trauma and Acute Care 2008;8(2):73‐77..
Nissman 2003 {published data only}
-
- Nissman SA, Kaplan LJ, Mann BD. Critically reappraising the literature‐driven practice of analgesia administration for acute abdominal pain in the emergency room prior to surgical evaluation.. Am J Surg 2003;185(4):291‐296.. - PubMed
Obermaier 2003 {published data only}
-
- Obermaier R, Benz S, Asgharnia M, Kirchner R, Hopt UT. Value of ultrasound in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis: interesting aspects. Eur J Med Res 2003;8(10):451‐456. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Orr 1995 {published data only}
-
- Orr RK, Porter D, Hartman D. Ultrasonography to evaluate adults for appendicitis: decision making based on meta‐analysis and probabilistic reasoning. Acad Emerg Med 1995;2(7):644‐650. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Oruc 2004 {published data only}
-
- Oruc MT, Kulah B, Ozozan O, Ozer V, Kulacoglu H, Turhan T, Coskun F. The value of 5‐hydroxy indole acetic acid measurement in spot urine in diagnosis of acute appendicitis. East Afr Med J 2004;81(1):40‐41. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Ranji 2006 {published data only}
-
- Ranji SR, Goldman LE, Simel DL, Shojania KG. Do opiates affect the clinical evaluation of patients with acute abdominal pain?. JAMA 2006;296(14):1764‐1774.. - PubMed
Rettenbacher 2002 {published data only}
-
- Rettenbacher T, Hollerweger A, Gritzmann N, Gotwald T, Schwamberger K, Ulmer H, Nedden DZ. Appendicitis: should diagnostic imaging be performed if the clinical presentation is highly suggestive of the disease?. Gastroenterology 2002;123(4):992‐998. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Sarfati 1993 {published data only}
-
- Sarfati MR, Hunter GC, Witzke DB, Bebb GG, Smythe SH, Boyan S, Rappaport WD. Impact of adjunctive testing on the diagnosis and clinical course of patients with acute appendicitis. Am J Surg 1993;166(6):660‐664. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Soda 2001 {published data only}
-
- Soda K, Nemoto K, Yoshizawa S, Hibiki T, Shizuya K, Konishi F. Detection of pinpoint tenderness on the appendix under ultrasonography is useful to confirm acute appendicitis. Arch Surg 2001;136(10):1136‐1140. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Steiner 2009 {published data only}
-
- Steiner TJ, Voelker M. Gastrointestinal tolerability of aspirin and the choice of over‐the‐counter analgesia for short‐lasting acute pain.. Journal of Clinical Pharmacy and Therapeutics 2009;34(2):177‐186.. - PubMed
Tait 1999 {published data only}
-
- Tait IS, Ionescu MV, Cuschieri A. Do patients with acute abdominal pain wait unduly long for analgesia?. J R Coll Surg Edinb 1999;44(3):181‐184. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Terasawa 2004 {published data only}
-
- Terasawa T, Blackmore CC, Bent S, Kohlwes RJ. Systematic review: computed tomography and ultrasonography to detect acute appendicitis in adults and adolescents. Ann Intern Med 2004;141(7):537‐546. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Thomas 1999 {published data only}
-
- Thomas SH, Borczuk P, Shackelford J, Ostrander J, Silver D, Evans M, Stein J. Patient and physician agreement on abdominal pain severity and need for opioid analgesia. Am J Emerg Med 1999;17(6):586‐590. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
van Dalen 2003 {published data only}
-
- Dalen R, Bagshaw PF, Dobbs BR, Robertson GM, Lynch AC, Frizelle FA. The utility of laparoscopy in the diagnosis of acute appendicitis in women of reproductive age. Surg Endosc 2003;17(8):1311‐1313. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Vane 2005 {published data only}
-
- Vane DW. Abdominal pain efficacy and concerns regarding early analgesia in children with acute abdominal pain.. Pediatrics 2005;116:1018.. - PubMed
Vermeulen 1995 {published data only}
-
- Vermeulen B, Morabia A, Unger PF. Influence of white cell count on surgical decision making in patients with abdominal pain in the right lower quadrant. Eur J Surg 1995;161(7):483‐486. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wolfe 2000 {published data only}
-
- Wolfe JM, Lein DY, Lenkoski K, Smithline HA. Analgesic administration to patients with an acute abdomen: a survey of emergency medicine physicians. Am J Emerg Med 2000;18(3):250‐253. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Wolfe 2004 {published data only}
-
- Wolfe JM, Smithline HA, Phipen S, Montano G, Garb JL, Fiallo V. Does morphine change the physical examination in patients with acute appendicitis?. Am J Emerg Med 2004;22(4):280‐285. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Additional references
Ahn 2002
-
- Ahn SH, Mayo‐Smith WW, Murphy BL, Reinert SE, Cronan JJ. Acute nontraumatic abdominal pain in adult patients: Abdominal radiography compared with CT evaluation. Radiology 2002;225:159‐164. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Camus‐Kerebel 1996
-
- Camus‐Kerebel C, Malledant Y, Joly A. Abdominal syndromes and analgesia. Can Anesthesiol 1996;44:335‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Jadad 1996
-
- Jadad AR, Moore RA, Carrol D. Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary? [Assessing the quality of reports of randomized clinical trials: is blinding necessary?]. Controlled Clin Trials 1996;17:1‐12. - PubMed
Kim 2003
-
- Kim MK, Galustyan S, Sato TT, Bergholte J, Hennes HM. Analgesia for Children With Acute Abdominal Pain: A Survey of Pediatric Emergency Physicians and Pediatric Surgeons. Pediatrics 2003;112:1122‐26. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Mahler 2004
-
- Mahler CW, Boermeester MA, Stoker J, Obertop H, Gouma DJ. Diagnostic modalities in diagnosis of adult patients with acute abdominal pain. Ned Tijdschr Geneeskd 2004;11(148):2474‐2480. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Stone 1998
-
- Stone R. Acute abdominal pain. Lippincotts Primary Care Practice 1998;2:341‐357. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Thomas 2003
-
- Thomas SH, Silen W. Effect on diagnostic efficiency of analgesia for undifferentiated abdominal pain. British Journal of Surgery 2003;90:5‐9. [MEDLINE: ] - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

