TDP-43 is a transcriptional repressor: the testis-specific mouse acrv1 gene is a TDP-43 target in vivo
- PMID: 21252238
- PMCID: PMC3064152
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.166587
TDP-43 is a transcriptional repressor: the testis-specific mouse acrv1 gene is a TDP-43 target in vivo
Abstract
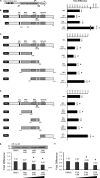
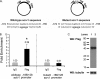
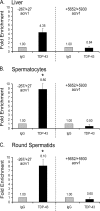
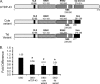
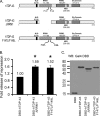
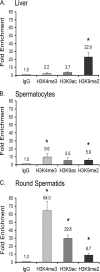
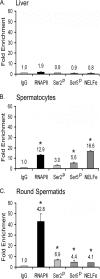
TDP-43 is an evolutionarily conserved ubiquitously expressed DNA/RNA-binding protein. Although recent studies have shown its association with a variety of neurodegenerative disorders, the function of TDP-43 remains poorly understood. Here we address TDP-43 function using spermatogenesis as a model system. We previously showed that TDP-43 binds to the testis-specific mouse acrv1 gene promoter in vitro via two GTGTGT-motifs and that mutation of these motifs led to premature transcription in spermatocytes of an otherwise round spermatid-specific promoter. The present study tested the hypothesis that TDP-43 represses acrv1 gene transcription in spermatocytes. Plasmid chromatin immunoprecipitation demonstrated that TDP-43 binds to the acrv1 promoter through GTGTGT motifs in vivo. Reporter gene assays showed that TDP-43 represses acrv1 core promoter-driven transcription via the N-terminal RRM1 domain in a histone deacetylase-independent manner. Consistent with repressor role, ChIP on physiologically isolated germ cells confirmed that TDP-43 occupies the endogenous acrv1 promoter in spermatocytes. Surprisingly, however, TDP-43 remains at the promoter in round spermatids, which express acrv1 mRNA. We show that RNA binding-defective TDP-43, but not splice variant isoforms, relieve repressor function. Transitioning from repressive to active histone marks has little effect on TDP-43 occupancy. Finally, we found that RNA polymerase II is recruited but paused at the acrv1 promoter in spermatocytes. Because mutation of TDP-43 sites caused premature transcription in spermatocytes in vivo, TDP-43 may be involved in pausing RNAPII at the acrv1 promoter in spermatocytes. Overall, our study shows that TDP-43 is a transcriptional repressor and that it regulates spatiotemporal expression of the acrv1 gene during spermatogenesis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Transcriptional regulation of spatiotemporal gene expression within the seminiferous epithelium: Mouse Acrv1 gene as a model.Andrology. 2023 Jul;11(5):904-910. doi: 10.1111/andr.13410. Epub 2023 Feb 24. Andrology. 2023. PMID: 36793255 Review.
-
Immunolocalization of TAR DNA-binding protein of 43 kDa (TDP-43) in mouse seminiferous epithelium.Mol Reprod Dev. 2017 Aug;84(8):675-685. doi: 10.1002/mrd.22851. Epub 2017 Jul 18. Mol Reprod Dev. 2017. PMID: 28600885 Free PMC article.
-
A novel CpG-free vertebrate insulator silences the testis-specific SP-10 gene in somatic tissues: role for TDP-43 in insulator function.J Biol Chem. 2007 Dec 14;282(50):36143-54. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M705811200. Epub 2007 Oct 11. J Biol Chem. 2007. PMID: 17932037
-
cis-requirement for the maintenance of round spermatid-specific transcription.Dev Biol. 2006 Jul 15;295(2):781-90. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2006.04.443. Epub 2006 May 3. Dev Biol. 2006. PMID: 16730344
-
Transcription and Splicing Factor TDP-43: Role in Regulation of Gene Expression in Testis.Semin Reprod Med. 2017 Mar;35(2):167-172. doi: 10.1055/s-0037-1599088. Epub 2017 Mar 9. Semin Reprod Med. 2017. PMID: 28278534 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
TDP-43 Epigenetic Facets and Their Neurodegenerative Implications.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 7;24(18):13807. doi: 10.3390/ijms241813807. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762112 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A novel long non-coding RNA Myolinc regulates myogenesis through TDP-43 and Filip1.J Mol Cell Biol. 2018 Apr 1;10(2):102-117. doi: 10.1093/jmcb/mjy025. J Mol Cell Biol. 2018. PMID: 29618024 Free PMC article.
-
The Molecular Link Between TDP-43, Endogenous Retroviruses and Inflammatory Neurodegeneration in Amyotrophic Lateral Sclerosis: a Potential Target for Triumeq, an Antiretroviral Therapy.Mol Neurobiol. 2023 Nov;60(11):6330-6345. doi: 10.1007/s12035-023-03472-y. Epub 2023 Jul 14. Mol Neurobiol. 2023. PMID: 37450244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Identification of cell-specific targets of sumoylation during mouse spermatogenesis.Reproduction. 2016 Feb;151(2):149-66. doi: 10.1530/REP-15-0239. Reproduction. 2016. PMID: 26701181 Free PMC article.
-
Opposing roles of p38α-mediated phosphorylation and PRMT1-mediated arginine methylation in driving TDP-43 proteinopathy.Cell Rep. 2025 Jan 28;44(1):115205. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.115205. Epub 2025 Jan 14. Cell Rep. 2025. PMID: 39817908 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Buratti E., Baralle F. E. (2008) Front. Biosci. 13, 867–878 - PubMed
-
- Neumann M., Sampathu D. M., Kwong L. K., Truax A. C., Micsenyi M. C., Chou T. T., Bruce J., Schuck T., Grossman M., Clark C. M., McCluskey L. F., Miller B. L., Masliah E., Mackenzie I. R., Feldman H., Feiden W., Kretzschmar H. A., Trojanowski J. Q., Lee V. M. (2006) Science 314, 130–133 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

