Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease
- PMID: 21252989
- PMCID: PMC3518031
- DOI: 10.1038/nri2921
Adipokines in inflammation and metabolic disease
Abstract
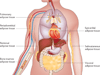
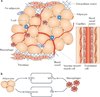
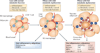
The worldwide epidemic of obesity has brought considerable attention to research aimed at understanding the biology of adipocytes (fat cells) and the events occurring in adipose tissue (fat) and in the bodies of obese individuals. Accumulating evidence indicates that obesity causes chronic low-grade inflammation and that this contributes to systemic metabolic dysfunction that is associated with obesity-linked disorders. Adipose tissue functions as a key endocrine organ by releasing multiple bioactive substances, known as adipose-derived secreted factors or adipokines, that have pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory activities. Dysregulated production or secretion of these adipokines owing to adipose tissue dysfunction can contribute to the pathogenesis of obesity-linked complications. In this Review, we focus on the role of adipokines in inflammatory responses and discuss their potential as regulators of metabolic function.
Figures
References
-
- Hotamisligil GS. Inflammation and metabolic disorders. Nature. 2006;444:860–867. - PubMed
-
- Ouchi N, Kihara S, Funahashi T, Matsuzawa Y, Walsh K. Obesity, adiponectin and vascular inflammatory disease. Curr. Opin. Lipidol. 2003;14:561–566. - PubMed
-
- Berg AH, Scherer PE. Adipose tissue, inflammation, and cardiovascular disease. Circ. Res. 2005;96:939–949. - PubMed
-
- Visser M, Bouter LM, McQuillan GM, Wener MH, Harris TB. Elevated C-reactive protein levels in overweight and obese adults. JAMA. 1999;282:2131–2135. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

