A case of thanatophoric dysplasia type I with an R248C mutation in the FGFR3 gene
- PMID: 21253318
- PMCID: PMC3021729
- DOI: 10.3345/kjp.2010.53.12.1022
A case of thanatophoric dysplasia type I with an R248C mutation in the FGFR3 gene
Abstract
Thanatophoric dysplasia (TD) is a short-limb neonatal dwarfism syndrome that is usually lethal in the perinatal period. It is characterized by shortening of the limbs, severely small thorax, large head with a prominent forehead, macrocephaly, curved femur, and flattened vertebral bodies. These malformations result from the mutation in fibroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR-3) gene which is located on the short arm of chromosome 4. A definite diagnosis should be established by molecular genetic analysis to find out the abnormal mutations in the FGFR3 gene. We confirmed by detection of a R248C mutation in the FGFR3 gene in DNA analysis.
Keywords: Fbroblast growth factor receptor 3 (FGFR3) gene; Thanatophoric dysplasia.
Figures
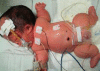
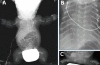

Similar articles
-
Identification of a novel insertion mutation in FGFR3 that causes thanatophoric dysplasia type 1.Am J Med Genet A. 2016 Jun;170(6):1573-9. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.a.37609. Epub 2016 Mar 30. Am J Med Genet A. 2016. PMID: 27028100
-
An R248C mutation of FGFR3 leading to thanatophoric dysplasia type I.Acta Paediatr Taiwan. 1999 Jul-Aug;40(4):262-4. Acta Paediatr Taiwan. 1999. PMID: 10910625
-
Rapid detection of common mutations of the FGFR3 gene causing thanatophoric dysplasia type I: two case reports.Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2012 Jun;31(3):128-33. doi: 10.3109/15513815.2011.648720. Epub 2012 Mar 13. Fetal Pediatr Pathol. 2012. PMID: 22414243
-
Prenatal diagnosis of hydrancephaly and enlarged cerebellum and cisterna magna in a fetus with thanatophoric dysplasia type II and a review of prenatal diagnosis of brain anomalies associated with thanatophoric dysplasia.Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2018 Feb;57(1):119-122. doi: 10.1016/j.tjog.2017.12.020. Taiwan J Obstet Gynecol. 2018. PMID: 29458880 Review.
-
The cerebral cortex malformation in thanatophoric dysplasia: neuropathology and pathogenesis.Acta Neuropathol. 2005 Sep;110(3):208-21. doi: 10.1007/s00401-005-1059-8. Acta Neuropathol. 2005. PMID: 16133544 Review.
Cited by
-
Lethal short limb dwarfism: thanatophoric dysplasia- type I.J Clin Diagn Res. 2014 Nov;8(11):PJ01-2. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2014/9195.5174. Epub 2014 Nov 20. J Clin Diagn Res. 2014. PMID: 25584280 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Fibroblast growth factor (FGF) signaling in development and skeletal diseases.Genes Dis. 2014 Dec 1;1(2):199-213. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2014.09.005. Genes Dis. 2014. PMID: 25679016 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Maroteaux P, Lamy M, Robert JM. Thanatophoric dwarfism. Presse Med. 1967;75:2519–2524. - PubMed
-
- Chen CP, Chern SR, Shih JC, Wang W, Yeh LF, Chang TY, et al. Prenatal diagnosis and genetic analysis of type I and type II thanatophoric dysplasia. Prenat Diagn. 2001;21:89–95. - PubMed
-
- Machado LE, Bonilla-Musoles F, Osborne NG. Thanatophoric dysplasia. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol. 2001;18:85–86. - PubMed
-
- Tsutsumi S, Sawai H, Nishimura G, Hayasaka K, Kurachi H. Prenatal diagnosis of thanatophoric dysplasia by 3-D helical computed tomography and genetic analysis. Fetal Diagn Ther. 2008;24:420–424. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

