Clinicopathologic features of metachronous or synchronous gastric cancer patients with three or more primary sites
- PMID: 21253324
- PMCID: PMC3021741
- DOI: 10.4143/crt.2010.42.4.217
Clinicopathologic features of metachronous or synchronous gastric cancer patients with three or more primary sites
Abstract
Purpose: We investigated the clinicopathologic information of patients with gastric cancer with multiple primary cancers (GC-MPC) of three or more sites.
Materials and methods: Between 1995 and 2009, 105,908 patients were diagnosed with malignancy at Severance Hospital, Yonsei University Health System. Of these, 113 (0.1%) patients with MPC of three or more sites were registered, and 41 (36.3%) of these were GC-MPC. We retrospectively reviewed the clinical data and overall survival using the medical records of these 41 GC-MPC patients. We defined synchronous cancers as those occurring within 6 months of the first primary cancer, while metachronous cancers were defined as those occurring more than 6 months later.
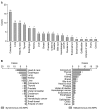
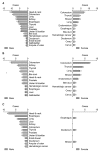
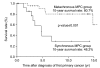
Results: Patients with metachronous GC-MPC were more likely to be female (p=0.003) and young than patients with synchronous GC-MPC (p=0.013). The most common cancer sites for metachronous GC-MPC patients were the colorectum, thyroid, lung, kidney and breast, while those for synchronous GC-MPC were the head and neck, esophagus, lung, and kidney. Metachronous GC-MPC demonstrated significantly better overall survival than synchronous GC-MPC, with median overall survival durations of 4.7 and 14.8 years, respectively, and 10-year overall survival rates of 48.2% and 80.7%, respectively (p<0.001).
Conclusion: Multiplicity of primary malignancies itself does not seem to indicate a poor prognosis. The early detection of additional primary malignancies will enable proper management with curative intent.
Keywords: Multiple primary; Neoplasms; Stomach neoplasms.
Figures
References
-
- Otsuji E, Yamaguchi T, Sawai K, Hagiwara A, Taniguchi H, Takahashi T. Recent advances in surgical treatment have improved the survival of patients with gastric carcinoma. Cancer. 1998;82:1233–1237. - PubMed
-
- Ikeda Y, Mori M, Koyanagi N, Wada H, Hayashi H, Tsugawa K, et al. Features of early gastric cancer detected by modern diagnostic technique. J Clin Gastroenterol. 1998;27:60–62. - PubMed
-
- Maehara Y, Okuyama T, Moriguchi S, Orita H, Kusumoto H, Korenaga D, et al. Prophylactic lymph node dissection in patients with advanced gastric cancer promotes increased survival time. Cancer. 1992;70:392–395. - PubMed
-
- Furukawa H, Hiratsuka M, Iwanaga T, Imaoka S, Kabuto T, Ishikawa O, et al. Treatments for second malignancies after gastrectomy for stomach cancer. Hepatogastroenterology. 1996;43:194–198. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

