Spatiotemporal analysis of multichannel EEG: CARTOOL
- PMID: 21253358
- PMCID: PMC3022183
- DOI: 10.1155/2011/813870
Spatiotemporal analysis of multichannel EEG: CARTOOL
Abstract
This paper describes methods to analyze the brain's electric fields recorded with multichannel Electroencephalogram (EEG) and demonstrates their implementation in the software CARTOOL. It focuses on the analysis of the spatial properties of these fields and on quantitative assessment of changes of field topographies across time, experimental conditions, or populations. Topographic analyses are advantageous because they are reference independents and thus render statistically unambiguous results. Neurophysiologically, differences in topography directly indicate changes in the configuration of the active neuronal sources in the brain. We describe global measures of field strength and field similarities, temporal segmentation based on topographic variations, topographic analysis in the frequency domain, topographic statistical analysis, and source imaging based on distributed inverse solutions. All analysis methods are implemented in a freely available academic software package called CARTOOL. Besides providing these analysis tools, CARTOOL is particularly designed to visualize the data and the analysis results using 3-dimensional display routines that allow rapid manipulation and animation of 3D images. CARTOOL therefore is a helpful tool for researchers as well as for clinicians to interpret multichannel EEG and evoked potentials in a global, comprehensive, and unambiguous way.
Figures
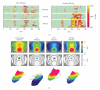
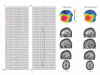
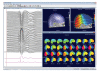

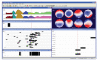

References
-
- Nunez PL, Srinivasan R. Electric Fields of the Brain: The Neurophysics of EEG. 2nd edition. New York, NY, USA: Oxford University Press; 2006.
-
- Vaughan HG. The neural origins of human event-related potentials. Annals of the New York Academy of Sciences. 1982;388:125–138. - PubMed
-
- Michel CM, Murray MM, Lantz G, Gonzalez S, Spinelli L, Grave De Peralta R. EEG source imaging. Clinical Neurophysiology. 2004;115(10):2195–2222. - PubMed
-
- Geselowitz DB. The zero of potential. IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Magazine. 1998;17(1):128–136. - PubMed
-
- Lehmann D, Skrandies W. Reference-free identification of components of checkerboard-evoked multichannel potential fields. Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology. 1980;48(6):609–621. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

