The traditional Japanese formula keishibukuryogan inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines by dermal endothelial cells
- PMID: 21253500
- PMCID: PMC3021874
- DOI: 10.1155/2010/804298
The traditional Japanese formula keishibukuryogan inhibits the production of inflammatory cytokines by dermal endothelial cells
Abstract
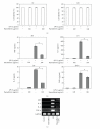
Keishibukuryogan (KBG) is one of the traditional herbal formulations widely administered to patients with blood stagnation for improving blood circulation; currently, it is the most frequently prescribed medicine in Japan. KBG has been reported to improve conjunctional microcirculation. The aim of this study was to evaluate the role of KBG and paeoniflorin, a bioactive compound of KBG, in inhibiting the production of inflammatory cytokines using human dermal microvessel endothelial cells (HDMECs). The authors observed that lipopolysaccharide (LPS; 1 μg/mL) stimulated the secretion of proinflammatory cytokines in HDMECs. KBG treatment (10 mg/mL) significantly suppressed the mRNA levels of migration inhibitory factor (MIF), interleukin (IL)-6, IL-8, and tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-α in LPS-stimulated cultured HDMECs. Similarly, paeoniflorin significantly suppressed the mRNA levels of these cytokines in LPS-stimulated cultured HDMECs. ELISA showed that KBG and paeoniflorin suppressed the production of MIF, IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α in LPS-stimulated HDMECs. Moreover, KBG and paeoniflorin decreased the expression of cyclooxygenase-2 and inducible nitric oxide synthase (iNOS) in these cells. These results suggest that KBG may be useful for improving microvascular inflammation in patients with skin diseases.
Figures


References
-
- Itoh T, Terasawa K, Kohta K, Shibahara N, Tosa H, Hiyama Y. Effects of Keishi-bukuryo-gan and Trapidil on the microcirculation in patients with cerebro-spinal vascular disease. Journal of Medical and Pharmaceutical Society for WAKAN-YAKU. 1992;9:40–46.
-
- Hikiami H, Goto H, Sekiya N, et al. Comparative efficacy of Keishi-bukuryo-gan and pentoxifylline on RBC deformability in patients with "oketsu" syndrome. Phytomedicine. 2003;10(6-7):459–466. - PubMed
-
- Kohta K, Hikiami H, Shimada Y, Matsuda H, Hamazaki T, Terasawa K. Effects of Keishi-bukuryo-gan on erythrocyte aggregability in patients with multiple old lacunar infarction. Journal of Medical and Pharmaceutical Society for WAKAN-YAKU. 1993;10:251–259.
-
- Tosa H, Toriizuka K, Terasawa K. The effect of Keishi-bukuryogan on blood viscosity and blood coagulation in normal subjects. Journal of Medical and Pharmaceutical Society for WAKAN-YAKU. 1987;4:172–179.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

