TCM Database@Taiwan: the world's largest traditional Chinese medicine database for drug screening in silico
- PMID: 21253603
- PMCID: PMC3017089
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015939
TCM Database@Taiwan: the world's largest traditional Chinese medicine database for drug screening in silico
Abstract
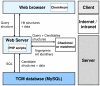
Rapid advancing computational technologies have greatly speeded up the development of computer-aided drug design (CADD). Recently, pharmaceutical companies have increasingly shifted their attentions toward traditional Chinese medicine (TCM) for novel lead compounds. Despite the growing number of studies on TCM, there is no free 3D small molecular structure database of TCM available for virtual screening or molecular simulation. To address this shortcoming, we have constructed TCM Database@Taiwan (http://tcm.cmu.edu.tw/) based on information collected from Chinese medical texts and scientific publications. TCM Database@Taiwan is currently the world's largest non-commercial TCM database. This web-based database contains more than 20,000 pure compounds isolated from 453 TCM ingredients. Both cdx (2D) and Tripos mol2 (3D) formats of each pure compound in the database are available for download and virtual screening. The TCM database includes both simple and advanced web-based query options that can specify search clauses, such as molecular properties, substructures, TCM ingredients, and TCM classification, based on intended drug actions. The TCM database can be easily accessed by all researchers conducting CADD. Over the last eight years, numerous volunteers have devoted their time to analyze TCM ingredients from Chinese medical texts as well as to construct structure files for each isolated compound. We believe that TCM Database@Taiwan will be a milestone on the path towards modernizing traditional Chinese medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures



References
-
- He M, Yan XJ, Zhou JJ, Xie GR. Traditional Chinese medicine database and application on the Web. J Chem Inf Comput Sci. 2001;41:273–277. - PubMed
-
- Qiao XB, Hou TJ, Zhang W, Guo SL, Xu SJ. A 3D structure database of components from Chinese traditional medicinal herbs. J Chem Inf Comput Sci. 2002;42:481–489. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

