c-Yes regulates cell adhesion at the blood-testis barrier and the apical ectoplasmic specialization in the seminiferous epithelium of rat testes
- PMID: 21256972
- PMCID: PMC3047590
- DOI: 10.1016/j.biocel.2011.01.008
c-Yes regulates cell adhesion at the blood-testis barrier and the apical ectoplasmic specialization in the seminiferous epithelium of rat testes
Abstract
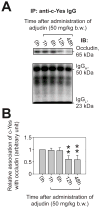
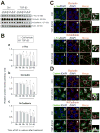
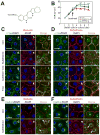
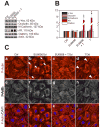
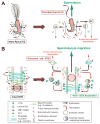
During spermatogenesis, extensive junction restructuring takes place at the blood-testis barrier (BTB) and the Sertoli cell-spermatid interface known as the apical ectoplasmic specialization (apical ES, a testis-specific adherens junction) in the seminiferous epithelium. However, the mechanism(s) that regulates these critical events in the testis remains unknown. Based on the current concept in the field, changes in the phosphorylation status of integral membrane proteins at these sites can induce alterations in protein endocytosis and recycling, causing junction restructuring. Herein, c-Yes, a non-receptor protein tyrosine kinase, was found to express abundantly at the BTB and apical ES stage-specifically, coinciding with junction restructuring events at these sites during the seminiferous epithelial cycle of spermatogenesis. c-Yes also structurally associated with adhesion proteins at the BTB (e.g., occludin and N-cadherin) and the apical ES (e.g., β1-integrin, laminins β3 and γ3), possibly to regulate phosphorylation status of proteins at these sites. SU6656, a selective c-Yes inhibitor, was shown to perturb the Sertoli cell tight junction-permeability barrier in vitro, which is mediated by changes in the distribution of occludin and N-cadherin at the cell-cell interface, moving from cell surface to cytosol, thereby destabilizing the tight junction-barrier. However, this disruptive effect of SU6656 on the barrier was blocked by testosterone. Furthermore, c-Yes is crucial to maintain the actin filament network in Sertoli cells since a blockade of c-Yes by SU6656 induced actin filament disorganization. In summary, c-Yes regulates BTB and apical ES integrity by maintaining proper distribution of integral membrane proteins and actin filament organization at these sites.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Boutros T, Chevet E, Metrakos P. Mitogen-activated protein (MAP) kinase/MAP kinase phosphatase regulation: Roles in cell growth, death, and cancer. Pharmacol Rev. 2008;60:261–310. - PubMed
-
- Cheng CY, Mruk DD. Cell junction dynamics in the testis: Sertoli-germ cell interactions and male contraceptive development. Physiol Rev. 2002;82:825–74. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

