Unusual heme-binding PAS domain from YybT family proteins
- PMID: 21257773
- PMCID: PMC3067658
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.01364-10
Unusual heme-binding PAS domain from YybT family proteins
Abstract
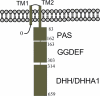
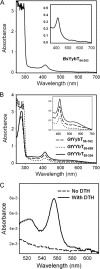
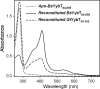
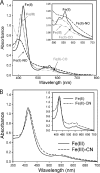
YybT family proteins (COG3887) are functionally unknown proteins that are widely distributed among the firmicutes, including the human pathogens Staphylococcus aureus and Listeria monocytogenes. Recent studies suggested that YybT family proteins are crucial for the in vivo survival of bacterial pathogens during host infection. YybT family proteins contain an N-terminal domain that shares minimum sequence homology with Per-ARNT-Sim (PAS) domains. Despite the lack of an apparent residue for heme coordination, the putative PAS domains of BsYybT and GtYybT, two representative members of the YybT family proteins from Bacillus subtilis and Geobacillus thermodenitrificans, respectively, are found to bind b-type heme with 1:1 stoichiometry. Heme binding suppresses the catalytic activity of the DHH/DHHA1 phosphodiesterase domain and the degenerate GGDEF domain. Absorption spectroscopic studies indicate that YybT proteins do not form stable oxyferrous complexes due to the rapid oxidation of the ferrous iron upon O(2) binding. The ferrous heme, however, forms a hexacoordinated complex with carbon monoxide (CO) and a pentacoordinated complex with nitric oxide (NO). The coordination of NO, but not CO, to the heme stimulates the phosphodiesterase activity. These results suggest that YybT family proteins function as stress-signaling proteins for monitoring cellular heme or the NO level by using a heme-binding PAS domain that features an unconventional heme coordination environment.
Figures
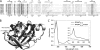
Similar articles
-
Solution structure of the PAS domain of a thermophilic YybT protein homolog reveals a potential ligand-binding site.J Biol Chem. 2013 Apr 26;288(17):11949-59. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.437764. Epub 2013 Mar 15. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 23504327 Free PMC article.
-
YybT is a signaling protein that contains a cyclic dinucleotide phosphodiesterase domain and a GGDEF domain with ATPase activity.J Biol Chem. 2010 Jan 1;285(1):473-82. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.040238. Epub 2009 Nov 9. J Biol Chem. 2010. PMID: 19901023 Free PMC article.
-
Dos, a heme-binding PAS protein from Escherichia coli, is a direct oxygen sensor.Biochemistry. 2000 Mar 14;39(10):2685-91. doi: 10.1021/bi991911s. Biochemistry. 2000. PMID: 10704219
-
Structural biology of heme binding in the Staphylococcus aureus Isd system.J Inorg Biochem. 2010 Mar;104(3):341-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jinorgbio.2009.09.012. Epub 2009 Sep 26. J Inorg Biochem. 2010. PMID: 19853304 Review.
-
Signal transduction by heme-containing PAS-domain proteins.J Appl Physiol (1985). 2004 Feb;96(2):774-83. doi: 10.1152/japplphysiol.00941.2003. J Appl Physiol (1985). 2004. PMID: 14715687 Review.
Cited by
-
Replenishing the cyclic-di-AMP pool: regulation of diadenylate cyclase activity in bacteria.Curr Genet. 2016 Nov;62(4):731-738. doi: 10.1007/s00294-016-0600-8. Epub 2016 Apr 13. Curr Genet. 2016. PMID: 27074767 Review.
-
DhhP, a cyclic di-AMP phosphodiesterase of Borrelia burgdorferi, is essential for cell growth and virulence.Infect Immun. 2014 May;82(5):1840-9. doi: 10.1128/IAI.00030-14. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Infect Immun. 2014. PMID: 24566626 Free PMC article.
-
A decade of research on the second messenger c-di-AMP.FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2020 Nov 24;44(6):701-724. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuaa019. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2020. PMID: 32472931 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bacterial Heme-Based Sensors of Nitric Oxide.Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018 Dec 20;29(18):1872-1887. doi: 10.1089/ars.2017.7235. Epub 2017 Sep 28. Antioxid Redox Signal. 2018. PMID: 28847157 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nano-RNases: oligo- or dinucleases?FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2022 Nov 2;46(6):fuac038. doi: 10.1093/femsre/fuac038. FEMS Microbiol Rev. 2022. PMID: 36026528 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Berry, E. A., and B. L. Trumpower. 1987. Simultaneous determination of hemes a, b, and c from pyridine hemochrome spectra. Anal. Biochem. 161:1-15. - PubMed
-
- Castiglione, N., S. Rinaldo, G. Giardina, and F. Cutruzzola. 2009. The transcription factor DNR from Pseudomonas aeruginosa specifically requires nitric oxide and haem for the activation of a target promoter in Escherichia coli. Microbiology 155:2838-2844. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

