CD4 and CD8 T cell immune activation during chronic HIV infection: roles of homeostasis, HIV, type I IFN, and IL-7
- PMID: 21257970
- PMCID: PMC7394280
- DOI: 10.4049/jimmunol.1002000
CD4 and CD8 T cell immune activation during chronic HIV infection: roles of homeostasis, HIV, type I IFN, and IL-7
Abstract
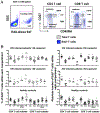
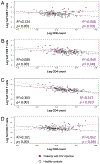
Immune activation plays an important role in the pathogenesis of HIV disease. Although the causes are not fully understood, the forces that lead to immune dysfunction differ for CD4 and CD8 T cells. In this study, we report that the molecular pathways that drive immune activation during chronic HIV infection are influenced by differences in the homeostatic regulation of the CD4 and CD8 T cell pools. Proliferation of CD4 T cells is controlled more tightly by CD4 T cell numbers than is CD8 T cell proliferation. This difference reflects the importance of maintaining a polyclonal CD4 T cell pool in host surveillance. Both pools of T cells were found to be driven by viral load and its associated state of inflammation. In the setting of HIV-induced lymphopenia, naive CD4 T cells were recruited mainly into the proliferating pool in response to CD4 T cell depletion, whereas naive CD8 T cell proliferation was driven mainly by levels of HIV RNA. RNA analysis revealed increased expression of genes associated with type I IFN and common γ chain cytokine signaling in CD4 T cell subsets and only type I IFN-associated genes in CD8 T cell subsets. In vitro studies demonstrated enhanced STAT1 phosphorylation in response to IFN-α and increased expression of the IFNAR1 transcripts in naive and memory CD4 T cells compared with that observed in CD8 T cells. CD4 T cell subsets also showed enhanced STAT1 phosphorylation in response to exogenous IL-7.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures
The authors have no financial conflicts of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Ho DD, Neumann AU, Perelson AS, Chen W, Leonard JM, and Markowitz M. 1995. Rapid turnover of plasma virions and CD4 lymphocytes in HIV-1 infection. Nature 373: 123–126. - PubMed
-
- Lempicki RA, Kovacs JA, Baseler MW, Adelsberger JW, Dewar RL, Natarajan V, Bosche MC, Metcalf JA, Stevens RA, Lambert LA, et al. 2000. Impact of HIV-1 infection and highly active antiretroviral therapy on the kinetics of CD4+ and CD8+ T cell turnover in HIV-infected patients. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 97: 13778–13783. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hazenberg MD, Hamann D, Schuitemaker H, and Miedema F. 2000. T cell depletion in HIV-1 infection: how CD4+ T cells go out of stock. Nat. Immunol 1: 285–289. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

