A highly parallel method for synthesizing DNA repeats enables the discovery of 'smart' protein polymers
- PMID: 21258353
- PMCID: PMC3075872
- DOI: 10.1038/nmat2942
A highly parallel method for synthesizing DNA repeats enables the discovery of 'smart' protein polymers
Abstract
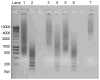
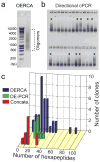
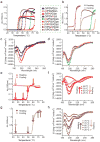
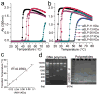
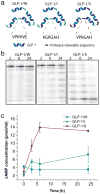
Robust high-throughput synthesis methods are needed to expand the repertoire of repetitive protein-polymers for different applications. To address this need, we developed a new method, overlap extension rolling circle amplification (OERCA), for the highly parallel synthesis of genes encoding repetitive protein-polymers. OERCA involves a single PCR-type reaction for the rolling circle amplification of a circular DNA template and simultaneous overlap extension by thermal cycling. We characterized the variables that control OERCA and demonstrated its superiority over existing methods, its robustness, high-throughput and versatility by synthesizing variants of elastin-like polypeptides (ELPs) and protease-responsive polymers of glucagon-like peptide-1 analogues. Despite the GC-rich, highly repetitive sequences of ELPs, we synthesized remarkably large genes without recursive ligation. OERCA also enabled us to discover 'smart' biopolymers that exhibit fully reversible thermally responsive behaviour. This powerful strategy generates libraries of repetitive genes over a wide and tunable range of molecular weights in a 'one-pot' parallel format.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
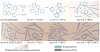
Comment in
-
Protein polymer: Gene libraries open up.Nat Mater. 2011 Feb;10(2):83-4. doi: 10.1038/nmat2955. Nat Mater. 2011. PMID: 21258347 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
-
- Simnick AJ, Lim DW, Chow D, Chilkoti A. Biomedical and biotechnological applications of elastin-like polypeptides. Polymer Reviews. 2007;47:121–154.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

