Application of a novel inhibitor of human CD59 for the enhancement of complement-dependent cytolysis on cancer cells
- PMID: 21258360
- PMCID: PMC4003131
- DOI: 10.1038/cmi.2010.35
Application of a novel inhibitor of human CD59 for the enhancement of complement-dependent cytolysis on cancer cells
Abstract
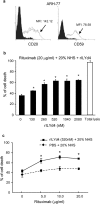
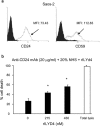
Many monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) have been extensively used in the clinic, such as rituximab to treat lymphoma. However, resistance and non-responsiveness to mAb treatment have been challenging for this line of therapy. Complement is one of the main mediators of antibody-based cancer therapy via the complement-dependent cytolysis (CDC) effect. CD59 plays a critical role in resistance to mAbs through the CDC effect. In this paper, we attempted to investigate whether the novel CD59 inhibitor, recombinant ILYd4, was effective in enhancing the rituximab-mediated CDC effect on rituximab-sensitive RL-7 lymphoma cells and rituximab-induced resistant RR51.2 cells. Meanwhile, the CDC effects, which were mediated by rituximab and anti-CD24 mAb, on the refractory multiple myeloma (MM) cell line ARH-77 and the solid tumor osteosarcoma cell line Saos-2, were respectively investigated. We found that rILYd4 rendered the refractory cells sensitive to the mAb-mediated CDC effect and that rILYd4 exhibited a synergistic effect with the mAb that resulted in tumor cells lysis. This effect on tumor cell lysis was apparent on both hematological tumors and solid tumors. Therefore, rILYd4 may serve as an adjuvant for mAb mediated-tumor immunotherapy.
Figures


Similar articles
-
rILYd4, a human CD59 inhibitor, enhances complement-dependent cytotoxicity of ofatumumab against rituximab-resistant B-cell lymphoma cells and chronic lymphocytic leukemia.Clin Cancer Res. 2011 Nov 1;17(21):6702-11. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-11-0647. Epub 2011 Sep 14. Clin Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21918174 Free PMC article.
-
Human CD59 inhibitor sensitizes rituximab-resistant lymphoma cells to complement-mediated cytolysis.Cancer Res. 2011 Mar 15;71(6):2298-307. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3016. Epub 2011 Jan 20. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21252115 Free PMC article.
-
Removal of the tag from His-tagged ILYd4, a human CD59 inhibitor, significantly improves its physical properties and its activity.Curr Pharm Des. 2012;18(27):4187-96. doi: 10.2174/138161212802430486. Curr Pharm Des. 2012. PMID: 22642361 Free PMC article.
-
Complement and cellular cytotoxicity in antibody therapy of cancer.Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008 Jun;8(6):759-68. doi: 10.1517/14712598.8.6.759. Expert Opin Biol Ther. 2008. PMID: 18476787 Review.
-
What signals are generated by anti-CD20 antibody therapy?Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2006 Dec;1(4):205-13. doi: 10.1007/s11899-006-0001-z. Curr Hematol Malig Rep. 2006. PMID: 20425315 Review.
Cited by
-
Transient removal of CD46 is safe and increases B-cell depletion by rituximab in CD46 transgenic mice and macaques.Mol Ther. 2013 Feb;21(2):291-9. doi: 10.1038/mt.2012.212. Epub 2012 Oct 23. Mol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23089733 Free PMC article.
-
Silencing of human phosphatidylethanolamine-binding protein 4 enhances rituximab-induced death and chemosensitization in B-cell lymphoma.PLoS One. 2013;8(2):e56829. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0056829. Epub 2013 Feb 25. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23451095 Free PMC article.
-
Extracellular Vesicles Isolated from Plasma of Multiple Myeloma Patients Treated with Daratumumab Express CD38, PD-L1, and the Complement Inhibitory Proteins CD55 and CD59.Cells. 2022 Oct 25;11(21):3365. doi: 10.3390/cells11213365. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36359760 Free PMC article.
-
Immunotherapy of cancer: from monoclonal to oligoclonal cocktails of anti-cancer antibodies: IUPHAR Review 18.Br J Pharmacol. 2016 May;173(9):1407-24. doi: 10.1111/bph.13450. Epub 2016 Mar 14. Br J Pharmacol. 2016. PMID: 26833433 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rapid degradation of the complement regulator, CD59, by a novel inhibitor.J Biol Chem. 2014 Apr 25;289(17):12109-12125. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.547083. Epub 2014 Mar 10. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 24616098 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Glennie MJ, French RR, Cragg MS, Taylor RP. Mechanisms of killing by anti-CD20 monoclonal antibodies. Mol Immunol. 2007;44:3823–3837. - PubMed
-
- Villamor N, Montserrat E, Colomer D. Mechanism of action and resistance to monoclonal antibody therapy. Semin Oncol. 2003;30:424–433. - PubMed
-
- Zhou X, Hu W, Qin X. The role of complement in the mechanism of action of rituximab for B-cell lymphoma: implications for therapy. Oncologist. 2008;13:954–966. - PubMed
-
- Morgan BP, Harris CL. Complement Regulatory Proteins. London; Academic Press; 1999.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

