Terahertz pulsed imaging of knee cartilage
- PMID: 21258522
- PMCID: PMC3018044
- DOI: 10.1364/BOE.1.000967
Terahertz pulsed imaging of knee cartilage
Abstract
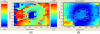
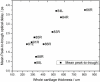
Osteoarthritis (OA) is a common form of arthritis caused by cartilage degeneration. In this paper, we investigate the potential use of terahertz (THz) pulsed imaging to quantitatively measure the early symptoms of OA in an animal model. THz images of excised rabbit femoral condyles were taken. We observe THz waves reflected off different layers within samples and demonstrate that the optical delay between reflections can give a quantitative measure of the thicknesses of particular tissues within cartilage.
Figures
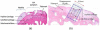



References
-
- “Osteoarthritis,” (NIH: National Institute of Arthritis and Musculoskeletal and Skin Diseases), http://www.nlm.nih.gov/medlineplus/osteoarthritis.html
-
- Poole A. R., Kojima T., Yasuda T., Mwale F., Kobayashi M., Laverty S., “Composition and structure of articular cartilage: a template for tissue repair,” Clin. Orthop. Relat. Res. (391 Suppl), S26–S33 (2001). - PubMed
-
- Arthritis Research UK , http://www.arthritisresearchuk.org/research/data_on_arthritis/data_on_oa...
-
- Mankin H., Dorfman H., Lippiell L., Zarins A., “Biochemical and metabolic abnormalities in articular cartilage from osteo-arthritic human hips. 2. correlation of morphology with biochemical and metabolic data,” J. Bone and Joint Surgery 53, 523–537 (1971). - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
