DESIGN AND PRELIMINARY VALIDATION OF A RAPID AUTOMATED BIODOSIMETRY TOOL FOR HIGH THROUGPUT RADIOLOGICAL TRIAGE
- PMID: 21258614
- PMCID: PMC3024000
- DOI: 10.1115/DETC2009-86425
DESIGN AND PRELIMINARY VALIDATION OF A RAPID AUTOMATED BIODOSIMETRY TOOL FOR HIGH THROUGPUT RADIOLOGICAL TRIAGE
Abstract
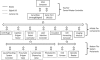
This paper presents design, hardware, software, and parameter optimization for a novel robotic automation system. RABiT is a Rapid Automated Biodosimetry Tool for high throughput radiological triage. The design considerations guiding the hardware and software architecture are presented with focus on methods of communication, ease of implementation, and need for real-time control versus soft time control cycles. The design and parameter determination for a non-contact PVC capillary laser cutting system is presented. A novel approach for lymphocyte concentration estimation based on computer vision is reported. Experimental evaluations of the system components validate the success of our prototype system in achieving a throughput of 6,000 samples in a period of 18 hours.
Figures












References
-
- Pellmar TC, Rockwell S. Priority list of research areas for radiological nuclear threat countermeasures. Radiation Research. 2005;163:115–123. - PubMed
-
- Meldrum DR, et al. Sample Preparation in Glass Capillaries for High-Throughput Biochemical Analyses. International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering; Edmonton, Canada. 2005.
-
- Prasanna PGS, et al. Technical Report. (AFRRI CD 05-2) Armed Forces Radiobiology Research Institute; 2005. Cytogenetic Biodosimetry for Radiation Disasters: Recent Advances.
-
- Soldatova LN, et al. An ontology for a robot scientist. Bioinformatics. 2006;22(14):464–471. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
