Proneurotrophin-3 may induce Sortilin-dependent death in inner ear neurons
- PMID: 21261755
- PMCID: PMC3078644
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1460-9568.2010.07556.x
Proneurotrophin-3 may induce Sortilin-dependent death in inner ear neurons
Abstract
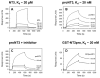
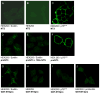
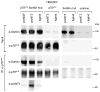
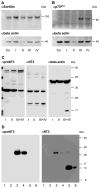
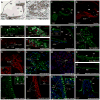
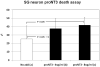
The precursor of the neurotrophin (NT) nerve growth factor (NGF) (proNGF) serves physiological functions distinct from its mature counterpart as it induces neuronal apoptosis through activation of a p75 NT receptor (p75(NTR) ) and Sortilin death-signalling complex. The NTs brain-derived nerve growth factor (BDNF) and NT3 provide essential trophic support to auditory neurons. Injury to the NT-secreting cells in the inner ear is followed by irreversible degeneration of spiral ganglion neurons with consequences such as impaired hearing or deafness. Lack of mature NTs may explain the degeneration of spiral ganglion neurons, but another mechanism is possible as unprocessed proNTs released from the injured cells may contribute to the degeneration by induction of apoptosis. Recent studies demonstrate that proBDNF, like proNGF, is a potent inducer of Sortilin:p75(NTR) -mediated apoptosis. In addition, a coincident upregulation of proBDNF and p75(NTR) has been observed in degenerating spiral ganglion neurons, but the Sortilin expression in the inner ear is unresolved. Here we demonstrate that Sortilin and p75(NTR) are coexpressed in neurons of the neonatal inner ear. Furthermore, we establish that proNT3 exhibits high-affinity binding to Sortilin and has the capacity to enhance cell surface Sortilin:p75(NTR) complex formation as well as to mediate apoptosis in neurons coexpressing p75(NTR) and Sortilin. Based on the examination of wildtype and Sortilin-deficient mouse embryos, Sortilin does not significantly influence the developmental selection of spiral ganglion neurons. However, our results suggest that proNT3 and proBDNF may play important roles in the response to noise-induced injuries or ototoxic damage via the Sortilin:p75(NTR) death-signalling complex.
© 2011 The Authors. European Journal of Neuroscience © 2011 Federation of European Neuroscience Societies and Blackwell Publishing Ltd.
Figures

Similar articles
-
p75(NTR) expression and nuclear localization of p75(NTR) intracellular domain in spiral ganglion Schwann cells following deafness correlate with cell proliferation.Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011 Aug;47(4):306-15. doi: 10.1016/j.mcn.2011.05.010. Epub 2011 May 30. Mol Cell Neurosci. 2011. PMID: 21658451 Free PMC article.
-
ProBDNF induces neuronal apoptosis via activation of a receptor complex of p75NTR and sortilin.J Neurosci. 2005 Jun 1;25(22):5455-63. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5123-04.2005. J Neurosci. 2005. PMID: 15930396 Free PMC article.
-
Interleukin-1β enhances neuronal vulnerability to proNGF-mediated apoptosis by increasing surface expression of p75(NTR) and sortillin.Neuroscience. 2014 Jan 17;257:11-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2013.10.058. Epub 2013 Nov 6. Neuroscience. 2014. PMID: 24211304 Free PMC article.
-
Dysregulation of proBDNF/p75NTR and BDNF/TrkB Signaling in Acute Ischemic Stroke: Different Sides of the Same Coins.Brain Res Bull. 2025 Jun 15;226:111338. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2025.111338. Epub 2025 Apr 8. Brain Res Bull. 2025. PMID: 40209946 Review.
-
The proNGF-p75NTR-sortilin signalling complex as new target for the therapeutic treatment of Parkinson's disease.CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008 Dec;7(6):512-23. doi: 10.2174/187152708787122923. CNS Neurol Disord Drug Targets. 2008. PMID: 19128208 Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping of the interaction site between sortilin and the p75 neurotrophin receptor reveals a regulatory role for the sortilin intracellular domain in p75 neurotrophin receptor shedding and apoptosis.J Biol Chem. 2012 Dec 21;287(52):43798-809. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M112.374710. Epub 2012 Oct 26. J Biol Chem. 2012. PMID: 23105113 Free PMC article.
-
The anti-apoptotic role of neurotensin.Cells. 2013 Mar 4;2(1):124-35. doi: 10.3390/cells2010124. Cells. 2013. PMID: 24709648 Free PMC article.
-
Organ of Corti explants direct tonotopically graded morphology of spiral ganglion neurons in vitro.J Comp Neurol. 2016 Aug 1;524(11):2182-207. doi: 10.1002/cne.23940. Epub 2015 Dec 25. J Comp Neurol. 2016. PMID: 26663318 Free PMC article.
-
Motoneuron programmed cell death in response to proBDNF.Dev Neurobiol. 2012 May;72(5):699-712. doi: 10.1002/dneu.20964. Dev Neurobiol. 2012. PMID: 21834083 Free PMC article.
-
Retrograde apoptotic signaling by the p75 neurotrophin receptor.Neuronal Signal. 2017 Feb 24;1(1):NS20160007. doi: 10.1042/NS20160007. eCollection 2017 Feb. Neuronal Signal. 2017. PMID: 32714573 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Brors D, Bodmer D, Pak K, Aletsee C, Schafers M, Dazert S, Ryan AF. EphA4 provides repulsive signals to developing cochlear ganglion neurites mediated through ephrin-B2 and -B3. J Comp Neurol. 2003;462:90–100. - PubMed
-
- Chao MV. Neurotrophins and their receptors: a convergence point for many signalling pathways. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003;4:299–309. - PubMed
-
- Ernfors P, Van De Water T, Loring J, Jaenisch R. Complementary roles of BDNF and NT-3 in vestibular and auditory development. Neuron. 1995;14:1153–1164. - PubMed
-
- Fritzsch B, Tessarollo L, Coppola E, Reichardt LF. Neurotrophins in the ear: their roles in sensory neuron survival and fiber guidance. Prog Brain Res. 2004;146:265–278. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

