Identification of the genes affecting the regulation of riboflavin synthesis in the flavinogenic yeast Pichia guilliermondii using insertion mutagenesis
- PMID: 21261808
- PMCID: PMC3495598
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1567-1364.2011.00720.x
Identification of the genes affecting the regulation of riboflavin synthesis in the flavinogenic yeast Pichia guilliermondii using insertion mutagenesis
Abstract
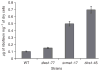
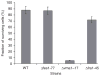
Pichia guilliermondii is a representative of a group of so-called flavinogenic yeast species that overproduce riboflavin (vitamin B(2)) in response to iron limitation. Using insertion mutagenesis, we isolated P. guilliermondii mutants overproducing riboflavin. Analysis of nucleotide sequence of recombination sites revealed that insertion cassettes integrated into the genome disrupting P. guilliermondii genes similar to the VMA1 gene of Ashbya gossypii and Saccharomyces cerevisiae and FES1 and FRA1 genes of S. cerevisiae. The constructed P. guilliermondiiΔvma1-17 mutant possessed five- to sevenfold elevated riboflavin production and twofold decreased iron cell content as compared with the parental strain. Pichia guilliermondiiΔfra1-45 mutant accumulated 1.8-2.2-fold more iron in the cells and produced five- to sevenfold more riboflavin as compared with the parental strain. Both Δvma1-17 and Δfes1-77 knockout strains could not grow at 37 °C in contrast to the wild-type strain and the Δfra1-45 mutant. Increased riboflavin production by the wild-type strain was observed at 37 °C. Although the Δfes1-77 mutant did not overproduce riboflavin, it showed partial complementation when crossed with previously isolated P. guilliermondii riboflavin-overproducing mutant rib80-22. Complementation analysis revealed that Δvma1-17 and Δfra1-45 mutants are distinct from previously reported riboflavin-producing mutants hit1-1, rib80-22 and rib81-31 of this yeast.
© 2011 Federation of European Microbiological Societies. Published by Blackwell Publishing Ltd. All rights reserved.
Figures


Similar articles
-
[Genetic control of riboflavin biosynthesis in Pichia guilliermondii yeasts. The detection of a new regulator gene RIB81].Genetika. 1985 Mar;21(3):368-74. Genetika. 1985. PMID: 3838729 Russian.
-
Positive selection of mutants defective in transcriptional repression of riboflavin synthesis by iron in the flavinogenic yeast Pichia guilliermondii.FEMS Yeast Res. 2005 Jun;5(9):829-37. doi: 10.1016/j.femsyr.2005.03.007. FEMS Yeast Res. 2005. PMID: 15925311
-
Mutations and environmental factors affecting regulation of riboflavin synthesis and iron assimilation also cause oxidative stress in the yeast Pichia guilliermondii.J Basic Microbiol. 2007 Oct;47(5):371-7. doi: 10.1002/jobm.200610279. J Basic Microbiol. 2007. PMID: 17910100
-
[Effect of rib83 mutation on riboflavin biosynthesis and iron assimilation in Pichia guilliermondii].Mikrobiologiia. 2001 Nov-Dec;70(6):753-8. Mikrobiologiia. 2001. PMID: 11785131 Russian.
-
[The red mutations impair the regulation of flavinogenesis and metal homeostas in yeast Pichia guilliermondii].Genetika. 2003 Aug;39(8):1026-32. Genetika. 2003. PMID: 14515457 Russian.
Cited by
-
Genetic control of biosynthesis and transport of riboflavin and flavin nucleotides and construction of robust biotechnological producers.Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011 Jun;75(2):321-60. doi: 10.1128/MMBR.00030-10. Microbiol Mol Biol Rev. 2011. PMID: 21646432 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Candida guilliermondii: biotechnological applications, perspectives for biological control, emerging clinical importance and recent advances in genetics.Curr Genet. 2013 Aug;59(3):73-90. doi: 10.1007/s00294-013-0391-0. Epub 2013 Apr 25. Curr Genet. 2013. PMID: 23616192
-
Whole genome sequencing and metabolomics analyses reveal the biosynthesis of nerol in a multi-stress-tolerant Meyerozyma guilliermondii GXDK6.Microb Cell Fact. 2021 Jan 3;20(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12934-020-01490-2. Microb Cell Fact. 2021. PMID: 33413399 Free PMC article.
-
Reliable differentiation of Meyerozyma guilliermondii from Meyerozyma caribbica by internal transcribed spacer restriction fingerprinting.BMC Microbiol. 2014 Feb 28;14:52. doi: 10.1186/1471-2180-14-52. BMC Microbiol. 2014. PMID: 24575831 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolic engineering of non-conventional yeasts for construction of the advanced producers of biofuels and high-value chemicals.BBA Adv. 2022 Dec 22;3:100071. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadva.2022.100071. eCollection 2023. BBA Adv. 2022. PMID: 37082251 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Boretsky Y, Kapustyak K, Fayura L, Stasyk O, Stenchuk M, Bobak Y, Drobot L, Sibirny A. Positive selection of mutants defective in transcriptional repression of riboflavin synthesis by iron in the flavinogenic yeast Pichia guilliermondii. FEMS Yeast Res. 2005;5:829–837. - PubMed
-
- Boretsky YR, Protchenko OV, Prokopiv TM, Mukalov IO, Fedorovych DV, Sibirny AA. Mutations and environmental factors affecting regulation of riboflavin synthesis and iron assimilation also cause oxidative stress in the yeast Pichia guilliermondii. J Basic Microb. 2007a;47:371–377. - PubMed
-
- Boretsky YR, Pynyaha YV, Boretsky VY, Kutsyaba VI, Protchenko OV, Philpott CC, Sibirny AA. Development of a transformation system for gene knock-out in the flavinogenic yeast Pichia guilliermondii. J Microbiol Meth. 2007b;70:13–19. - PubMed
-
- Boretsky YR, Voronovsky AA, Liauta-Tehlivets OY, Hasslacher M, Kohlwein SD, Shavlovsky GM. Identification of an ARS element and development of a high efficiency transformation system for Pichia guilliermondii. Curr Genet. 1999;36:215–221. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

