Peroxiredoxin 6 phosphorylation and subsequent phospholipase A2 activity are required for agonist-mediated activation of NADPH oxidase in mouse pulmonary microvascular endothelium and alveolar macrophages
- PMID: 21262967
- PMCID: PMC3064221
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M110.206623
Peroxiredoxin 6 phosphorylation and subsequent phospholipase A2 activity are required for agonist-mediated activation of NADPH oxidase in mouse pulmonary microvascular endothelium and alveolar macrophages
Abstract
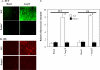
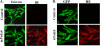
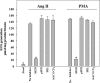
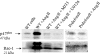
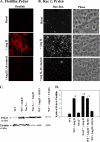
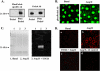
Peroxiredoxin 6 (Prdx6), a bifunctional enzyme with glutathione peroxidase and phospholipase A2 (PLA(2)) activities, participates in the activation of NADPH oxidase 2 (NOX2) in neutrophils, but the mechanism for this effect is not known. We now demonstrate that Prdx6 is required for agonist-induced NOX2 activation in pulmonary microvascular endothelial cells (PMVEC) and that the effect requires the PLA(2) activity of Prdx6. Generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) in response to angiotensin II (Ang II) or phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate was markedly reduced in perfused lungs and isolated PMVEC from Prdx6 null mice. Rac1 and p47(phox), cytosolic components of NOX2, translocated to the endothelial cell membrane after Ang II treatment in wild-type but not Prdx6 null PMVEC. MJ33, an inhibitor of Prdx6 PLA(2) activity, blocked agonist-induced PLA(2) activity and ROS generation in PMVEC by >80%, whereas inhibitors of other PLA(2)s were ineffective. Transfection of Prx6 null cells with wild-type and C47S mutant Prdx6, but not with mutants of the PLA(2) active site (S32A, H26A, and D140A), "rescued" Ang II-induced PLA(2) activity and ROS generation. Ang II treatment of wild-type cells resulted in phosphorylation of Prdx6 and its subsequent translocation from the cytosol to the cell membrane. Phosphorylation as well as PLA(2) activity and ROS generation were markedly reduced by the MAPK inhibitor, U0126. Thus, agonist-induced MAPK activation leads to Prdx6 phosphorylation and translocation to the cell membrane, where its PLA(2) activity facilitates assembly of the NOX2 complex and activation of the oxidase.
Figures



References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

