Clinical and molecular pharmacology of etomidate
- PMID: 21263301
- PMCID: PMC3108152
- DOI: 10.1097/ALN.0b013e3181ff72b5
Clinical and molecular pharmacology of etomidate
Abstract
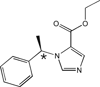
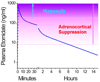
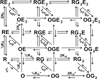
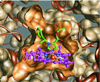
This review focuses on the unique clinical and molecular pharmacologic features of etomidate. Among general anesthesia induction drugs, etomidate is the only imidazole, and it has the most favorable therapeutic index for single-bolus administration. It also produces a unique toxicity among anesthetic drugs: inhibition of adrenal steroid synthesis that far outlasts its hypnotic action and that may reduce survival of critically ill patients. The major molecular targets mediating anesthetic effects of etomidate in the central nervous system are specific γ-aminobutyric acid type A receptor subtypes. Amino acids forming etomidate binding sites have been identified in transmembrane domains of these proteins. Etomidate binding site structure models for the main enzyme mediating etomidate adrenotoxicity have also been developed. Based on this deepening understanding of molecular targets and actions, new etomidate derivatives are being investigated as potentially improved sedative-hypnotics or for use as highly selective inhibitors of adrenal steroid synthesis.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures


References
-
- Godefroi EF, Janssen PAJ, Van der Eycken CAM, Van Heertum AHMT, Niemegeers CJE. DL-(1-arylalkyl)imidazole-5-carboxylate esters. A novel type of hypnotic agents. J Med Chem. 1965;56:220–223. - PubMed
-
- Tomlin SL, Jenkins A, Lieb WR, Franks NP. Stereoselective effects of etomidate optical isomers on gamma- aminobutyric acid type A receptors and animals. Anesthesiology. 1998;88:708–717. - PubMed
-
- Husain SS, Ziebell MR, Ruesch D, Hong F, Arevalo E, Kosterlitz JA, Olsen RW, Forman SA, Cohen JB, Miller KW. 2-(3-Methyl-3H-diaziren-3-yl)ethyl 1-(1-phenylethyl)-1H-imidazole-5-carboxylate: A derivative of the stereoselective general anesthetic etomidate for photolabeling ligand-gated ion channels. J Med Chem. 2003;46:1257–1265. - PubMed
-
- Janssen PA, Niemegeers CJ, Schellekens KH, Lenaerts FM. Etomidate, R-(+)-ethyl-1-(-methyl-benzyl)imidazole-5-carboxylate (R 16659): A potent, short-acting and relatively atoxic intravenous hypnotic agent in rats. Arzneimittelforschung. 1971;21:1234–1243. - PubMed
-
- Janssen PA, Niemegeers CJ, Marsboom RP. Etomidate, a potent non-barbiturate hypnotic: Intravenous etomidate in mice, rats, guinea-pigs, rabbits and dogs. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther. 1975;214:92–132. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical

