Spatial light interference microscopy (SLIM)
- PMID: 21263640
- PMCID: PMC3482902
- DOI: 10.1364/OE.19.001016
Spatial light interference microscopy (SLIM)
Abstract
We present spatial light interference microscopy (SLIM) as a new optical microscopy technique, capable of measuring nanoscale structures and dynamics in live cells via interferometry. SLIM combines two classic ideas in light imaging: Zernike's phase contrast microscopy, which renders high contrast intensity images of transparent specimens, and Gabor's holography, where the phase information from the object is recorded. Thus, SLIM reveals the intrinsic contrast of cell structures and, in addition, renders quantitative optical path-length maps across the sample. The resulting topographic accuracy is comparable to that of atomic force microscopy, while the acquisition speed is 1,000 times higher. We illustrate the novel insight into cell dynamics via SLIM by experiments on primary cell cultures from the rat brain. SLIM is implemented as an add-on module to an existing phase contrast microscope, which may prove instrumental in impacting the light microscopy field at a large scale.
Figures
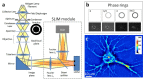
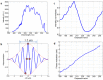
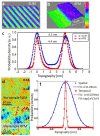
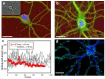

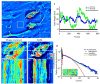
References
-
- G. Popescu, “Quantitative phase imaging of nanoscale cell structure and dynamics,” in Methods in Cell Biology, P. J. Bhanu, ed. (Elsevier, 2008), p. 87. - PubMed
-
- Paganin D., Nugent K. A., “Noninterferometric phase imaging with partially coherent light,” Phys. Rev. Lett. 80(12), 2586–2589 (1998). 10.1103/PhysRevLett.80.2586 - DOI
-
- Zicha D., Dunn G. A., “An Image-Processing System For Cell Behavior Studies In Subconfluent Cultures,” J. Microsc. 179, 11–21 (1995). 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1995.tb03609.x - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials

