A broadly flavivirus cross-neutralizing monoclonal antibody that recognizes a novel epitope within the fusion loop of E protein
- PMID: 21264311
- PMCID: PMC3019176
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0016059
A broadly flavivirus cross-neutralizing monoclonal antibody that recognizes a novel epitope within the fusion loop of E protein
Abstract
Flaviviruses are a group of human pathogenic, enveloped RNA viruses that includes dengue (DENV), yellow fever (YFV), West Nile (WNV), and Japanese encephalitis (JEV) viruses. Cross-reactive antibodies against Flavivirus have been described, but most of them are generally weakly neutralizing. In this study, a novel monoclonal antibody, designated mAb 2A10G6, was determined to have broad cross-reactivity with DENV 1-4, YFV, WNV, JEV, and TBEV. Phage-display biopanning and structure modeling mapped 2A10G6 to a new epitope within the highly conserved flavivirus fusion loop peptide, the (98)DRXW(101) motif. Moreover, in vitro and in vivo experiments demonstrated that 2A10G6 potently neutralizes DENV 1-4, YFV, and WNV and confers protection from lethal challenge with DENV 1-4 and WNV in murine model. Furthermore, functional studies revealed that 2A10G6 blocks infection at a step after viral attachment. These results define a novel broadly flavivirus cross-reactive mAb with highly neutralizing activity that can be further developed as a therapeutic agent against severe flavivirus infections in humans.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
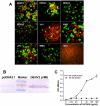

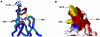
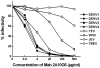
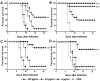
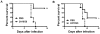
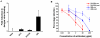
References
-
- Mackenzie JS, Gubler DJ, Petersen LR. Emerging flaviviruses: the spread and resurgence of Japanese encephalitis, West Nile and dengue viruses. Nat Med. 2004;10:S98–S109. - PubMed
-
- Gould EA, Solomon T. Pathogenic flaviviruses. Lancet. 2008;371:500–509. - PubMed
-
- Roehrig JT, Staudinger LA, Hunt AR, Mathews JH, Blair CD. Antibody prophylaxis and therapy for flaviviral encephalitis infections. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2001;951:286–297. - PubMed
-
- Morrey JD, Siddharthan V, Olsen AL, Roper GY, Wang H, et al. Humanized monoclonal antibody against West Nile virus envelope protein administered after neuronal infection protects against lethal encephalitis in hamsters. J Infect Dis. 2006;194:1300–1308. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

