The role of subjective frequency in language switching: an ERP investigation using masked priming
- PMID: 21264577
- PMCID: PMC3331680
- DOI: 10.3758/s13421-010-0006-7
The role of subjective frequency in language switching: an ERP investigation using masked priming
Abstract
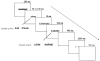
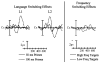
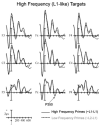
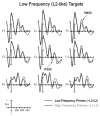
Two experiments examined the nature of language-switching effects in a priming paradigm with event-related brain potential (ERP) recordings. primes and targets were always unrelated words but could be either from the same or different languages (Experiment 1) or from the same or a different frequency range (Experiment 2). Effects of switching language across prime and target differed as a function of the direction of the switch and prime duration in Experiment 1. Effects tended to be stronger with 100-ms prime durations than with 50-ms durations, and the expected pattern of greater negativity in the switch condition appeared earlier when primes were in L1 and targets in L2 than vice versa. Experiment 2 examined whether these language-switching effects could be due to differences in the subjective frequency of words in a bilingual's two languages, by testing a frequency-switching manipulation within the L1. Effects of frequency switching were evident in the ERP waveforms, but the pattern did not resemble the language-switching effects, therefore suggesting that different mechanisms are at play.
Figures




References
-
- Alvarez RP, Holcomb PJ, Grainger J. Accessing word meaning in two languages: An event-related brain potential study of beginning bilinguals. Brain and Language. 2003;87:290–304. - PubMed
-
- Costa A, Santesteban M. Lexical access in bilingual speech production: Evidence from language-switching in highly proficient bilinguals and L2 learners. Journal of Memory and Language. 2004;50:491–511.
-
- Dalrymple-Alford EC. Language-switching during bilingual reading. British Journal of Psychology. 1985;76:111–122.
-
- Dijkstra T, van Heuven WJB. The architecture of the bilingual word recognition system: From identification to decision. Bilingualism: Language & Cognition. 2002;5:175–197.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

