Neural and behavioral effects of interference resolution in depression and rumination
- PMID: 21264648
- PMCID: PMC4006074
- DOI: 10.3758/s13415-010-0014-x
Neural and behavioral effects of interference resolution in depression and rumination
Abstract
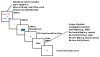
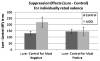
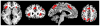
Individuals diagnosed with major depressive disorder (MDD) often ruminate about their depression and their life situations, impairing their concentration and performance on daily tasks. We examined whether rumination might be due to a deficit in the ability to expel negative information from short-term memory (STM), and fMRI was used to examine the neural structures involved in this ability. MDD and healthy control (HC) participants were tested using a directed-forgetting procedure in a short-term item recognition task. As predicted, MDD participants had more difficulty than did HCs in expelling negative, but not positive, words from STM. Overall, the neural networks involved in directed forgetting were similar for both groups, but the MDDs exhibited more spatial variability in activation in the left inferior frontal gyrus (a region critical for inhibiting irrelevant information), which may contribute to their relative inability to inhibit negative information.
Figures

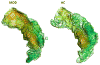
References
-
- Anderson MC, Green C. Suppressing unwanted memories by executive control. Nature. 2001;410:366–369. - PubMed
-
- Beck AT. Depression: Clinical, experimental and theoretical aspects. New York: Harper & Row; 1967.
-
- Beck AT, Steer RA, Brown GK. Manual for the beck depression inventory–II. San Antonio, TX: Psychological Corp; 1996.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

