Ketamine inhibits tumor necrosis factor secretion by RAW264.7 murine macrophages stimulated with antibiotic-exposed strains of community-associated, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
- PMID: 21266054
- PMCID: PMC3037927
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2172-12-11
Ketamine inhibits tumor necrosis factor secretion by RAW264.7 murine macrophages stimulated with antibiotic-exposed strains of community-associated, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus
Abstract
Background: Infections caused by community-associated strains of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (CA-MRSA) are associated with a marked and prolonged host inflammatory response. In a sepsis simulation model, we tested whether the anesthetic ketamine inhibits the macrophage TNF response to antibiotic-exposed CA-MRSA bacteria via its antagonism of N-methyl-D-aspartate (NMDA) receptors. RAW264.7 cells were stimulated for 18 hrs with 105 to 107 CFU/mL inocula of either of two prototypical CA-MRSA isolates, USA300 strain LAC and USA400 strain MW2, in the presence of either vancomycin or daptomycin. One hour before bacterial stimulation, ketamine was added with or without MK-801 (dizocilpine, a chemically unrelated non-competitive NMDA receptor antagonist), APV (D-2-amino-5-phosphono-valerate, a competitive NMDA receptor antagonist), NMDA, or combinations of these agents. Supernatants were collected and assayed for TNF concentration by ELISA.
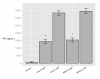
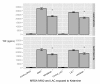
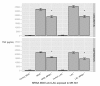
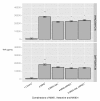
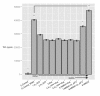
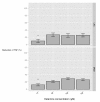
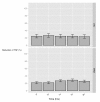
Results: RAW264.7 cells exposed to either LAC or MW2 in the presence of daptomycin secreted less TNF than in the presence of vancomycin. The addition of ketamine inhibited macrophage TNF secretion after stimulation with either of the CA-MRSA isolates (LAC, MW2) in the presence of either antibiotic. The NMDA inhibitors, MK-801 and APV, also suppressed macrophage TNF secretion after stimulation with either of the antibiotic-exposed CA-MRSA isolates, and the effect was not additive or synergistic with ketamine. The addition of NMDA substrate augmented TNF secretion in response to the CA-MRSA bacteria, and the addition of APV suppressed the effect of NMDA in a dose-dependent fashion.
Conclusions: Ketamine inhibits TNF secretion by MRSA-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages and the mechanism likely involves NMDA receptor antagonism. These findings may have therapeutic significance in MRSA sepsis.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Rapamycin Augments the NMDA-Mediated TNF Suppression of MRSA-Stimulated RAW264.7 Murine Macrophages.Int J Inflam. 2012;2012:542727. doi: 10.1155/2012/542727. Epub 2012 Oct 10. Int J Inflam. 2012. PMID: 23094196 Free PMC article.
-
Role of bacterial components in macrophage activation by the LAC and MW2 strains of community-associated, methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus.Cell Immunol. 2011;269(1):46-53. doi: 10.1016/j.cellimm.2011.03.009. Epub 2011 Mar 15. Cell Immunol. 2011. PMID: 21458780
-
In Vitro Synergistic Effect of Vancomycin and Some Antibacterial Agents Against Clinical Methicillin-Resistant and Sensitive Staphylococcus aureus Isolates.Microb Drug Resist. 2020 Mar;26(3):218-226. doi: 10.1089/mdr.2019.0003. Epub 2019 Aug 19. Microb Drug Resist. 2020. PMID: 31424323
-
Emergence of daptomycin resistance following vancomycin-unresponsive Staphylococcus aureus bacteraemia in a daptomycin-naïve patient--a review of the literature.Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011 May;30(5):603-10. doi: 10.1007/s10096-010-1128-3. Epub 2010 Dec 30. Eur J Clin Microbiol Infect Dis. 2011. PMID: 21191627 Review.
-
Bacteremia due to Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus aureus: An Update on New Therapeutic Approaches.Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2020 Dec;34(4):849-861. doi: 10.1016/j.idc.2020.04.003. Epub 2020 Sep 30. Infect Dis Clin North Am. 2020. PMID: 33011050 Review.
Cited by
-
Respiratory gas exchange as a new aid to monitor acidosis in endotoxemic rats: relationship to metabolic fuel substrates and thermometabolic responses.Physiol Rep. 2017 Jan;5(1):e13100. doi: 10.14814/phy2.13100. Physiol Rep. 2017. PMID: 28082427 Free PMC article.
-
Protective Effect of Dizocilpine (MK-801) On TNBS-Induced Experimental Colitis in Mice.Iran J Pharm Res. 2019 Summer;18(3):1341-1850. doi: 10.22037/ijpr.2019.1100751. Iran J Pharm Res. 2019. PMID: 32641944 Free PMC article.
-
Ketamine inhibits calcium elevation and hydroxyl radical and nitric oxide production in lipopolysaccharide-stimulated NR8383 alveolar macrophages.Inflammation. 2013 Oct;36(5):1094-100. doi: 10.1007/s10753-013-9642-y. Inflammation. 2013. PMID: 23595868
-
Dialkyl Carbamoyl Chloride-Coated Dressing Prevents Macrophage and Fibroblast Stimulation via Control of Bacterial Growth: An In Vitro Assay.Microorganisms. 2022 Sep 13;10(9):1825. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms10091825. Microorganisms. 2022. PMID: 36144427 Free PMC article.
-
Ketamine promotes inflammation through increasing TLR4 expression in RAW264.7 cells.J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2015 Jun;35(3):419-425. doi: 10.1007/s11596-015-1447-9. Epub 2015 Jun 14. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci. 2015. PMID: 26072083
References
-
- Buckingham SC, McDougal LK, Cathey LD, Comeaux K, Craig AS, Fridkin SK, Tenover FC. Emergence of community-associated methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus at a Memphis, Tennessee children's hospital. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2004;23:619–24. doi: 10.1097/01.inf.0000131981.67342.c4. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Klevens RM, Morrison MA, Nadle J, Petit S, Gershman K, Ray S, Harrison LH, Lynfield R, Dumyati G, Townes JM, Craig AS, Zell ER, Fosheim GE, McDougal LK, Carey RB, Fridkin SK. Invasive methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus infections in the United States. Jama. 2007;298:1763–71. doi: 10.1001/jama.298.15.1763. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention: Four pediatric deaths from community-acquired methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus--Minnesota and North Dakota, 1997-1999. MMWR. 1999;48:707–710. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

