Pathophysiology, treatment, and animal and cellular models of human ischemic stroke
- PMID: 21266064
- PMCID: PMC3037909
- DOI: 10.1186/1750-1326-6-11
Pathophysiology, treatment, and animal and cellular models of human ischemic stroke
Abstract
Stroke is the world's second leading cause of mortality, with a high incidence of severe morbidity in surviving victims. There are currently relatively few treatment options available to minimize tissue death following a stroke. As such, there is a pressing need to explore, at a molecular, cellular, tissue, and whole body level, the mechanisms leading to damage and death of CNS tissue following an ischemic brain event. This review explores the etiology and pathogenesis of ischemic stroke, and provides a general model of such. The pathophysiology of cerebral ischemic injury is explained, and experimental animal models of global and focal ischemic stroke, and in vitro cellular stroke models, are described in detail along with experimental strategies to analyze the injuries. In particular, the technical aspects of these stroke models are assessed and critically evaluated, along with detailed descriptions of the current best-practice murine models of ischemic stroke. Finally, we review preclinical studies using different strategies in experimental models, followed by an evaluation of results of recent, and failed attempts of neuroprotection in human clinical trials. We also explore new and emerging approaches for the prevention and treatment of stroke. In this regard, we note that single-target drug therapies for stroke therapy, have thus far universally failed in clinical trials. The need to investigate new targets for stroke treatments, which have pleiotropic therapeutic effects in the brain, is explored as an alternate strategy, and some such possible targets are elaborated. Developing therapeutic treatments for ischemic stroke is an intrinsically difficult endeavour. The heterogeneity of the causes, the anatomical complexity of the brain, and the practicalities of the victim receiving both timely and effective treatment, conspire against developing effective drug therapies. This should in no way be a disincentive to research, but instead, a clarion call to intensify efforts to ameliorate suffering and death from this common health catastrophe. This review aims to summarize both the present experimental and clinical state-of-the art, and to guide future research directions.
Figures
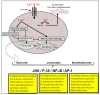
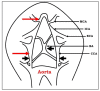
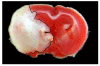
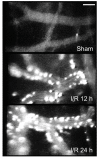
References
-
- WHO Global Infobase. https://apps.who.int/infobase/Mortality.aspx
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

