Chatting histone modifications in mammals
- PMID: 21266346
- PMCID: PMC3080777
- DOI: 10.1093/bfgp/elq024
Chatting histone modifications in mammals
Abstract
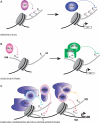
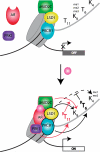
Eukaryotic chromatin can be highly dynamic and can continuously exchange between an open transcriptionally active conformation and a compacted silenced one. Post-translational modifications of histones have a pivotal role in regulating chromatin states, thus influencing all chromatin dependent processes. Methylation is currently one of the best characterized histone modification and occurs on arginine and lysine residues. Histone methylation can regulate other modifications (e.g. acetylation, phosphorylation and ubiquitination) in order to define a precise functional chromatin environment. In this review we focus on histone methylation and demethylation, as well as on the enzymes responsible for setting these marks. In particular we are describing novel concepts on the interdependence of histone modifications marks and discussing the molecular mechanisms governing this cross-talks.
Figures
References
-
- Luger K, Rechsteiner TJ, Flaus AJ, et al. Characterization of nucleosome core particles containing histone proteins made in bacteria. J Mol Biol. 1997;272(3):301–11. - PubMed
-
- Kunert N, Brehm A. Novel Mi-2 related ATP-dependent chromatin remodelers. Epigenetics. 2009;4(4):209–11. - PubMed
-
- Talbert PB, Henikoff S. Histone variants–ancient wrap artists of the epigenome. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2010;11(4):264–75. - PubMed
-
- Kouzarides T. Chromatin modifications and their function. Cell. 2007;128(4):693–705. - PubMed
-
- Campos EI, Reinberg D. Histones: annotating chromatin. Annu Rev Genet. 2009;43:559–99. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

