The effect of membrane curvature on the conformation of antimicrobial peptides: implications for binding and the mechanism of action
- PMID: 21267557
- PMCID: PMC3070085
- DOI: 10.1007/s00249-011-0677-4
The effect of membrane curvature on the conformation of antimicrobial peptides: implications for binding and the mechanism of action
Abstract
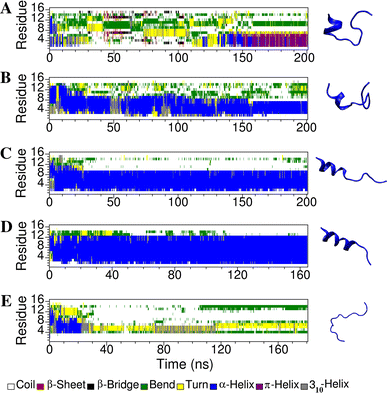
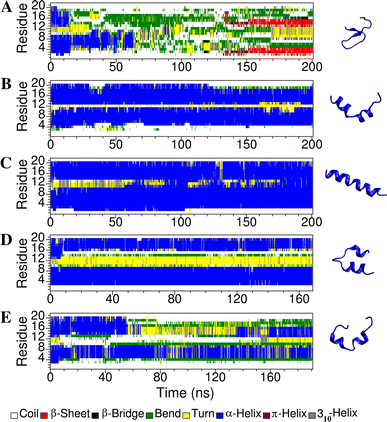
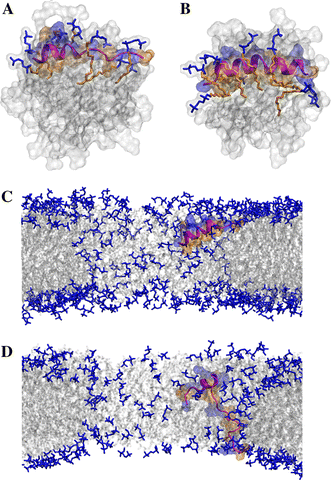
Short cationic antimicrobial peptides (AMPs) are believed to act either by inducing transmembrane pores or disrupting membranes in a detergent-like manner. For example, the antimicrobial peptides aurein 1.2, citropin 1.1, maculatin 1.1 and caerin 1.1, despite being closely related, appear to act by fundamentally different mechanisms depending on their length. Using molecular dynamics simulations, the structural properties of these four peptides have been examined in solution as well as in a variety of membrane environments. It is shown that each of the peptides has a strong preference for binding to regions of high membrane curvature and that the structure of the peptides is dependent on the degree of local curvature. This suggests that the shorter peptides aurein 1.2 and citropin 1.1 act via a detergent-like mechanism because they can induce high local, but not long-range curvature, whereas the longer peptides maculatin 1.1 and caerin 1.1 require longer range curvature to fold and thus bind to and stabilize transmembrane pores.
Figures

References
-
- Anézo C, de Vries AH, Höltje HD, Tieleman DP, Marrink S-J. Methodological issues in lipid bilayer simulations. J Phys Chem B. 2003;107:9424–9433. doi: 10.1021/jp0348981. - DOI
-
- Apponyi MA, Pukala TL, Brinkworth CS, Maselli VM, Bowie JH, Tyler MJ, Booker GW, Wallace JC, Carver JA, Separovic F, Doyle J, Llewellyn LE. Host-defence peptides of Australian anurans: structure, mechanism of action and evolutionary significance. Peptides. 2004;25:1035–1054. doi: 10.1016/j.peptides.2004.03.006. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

