New insights into the inactivation of gastric tumor suppressor RUNX3: the role of H. pylori infection
- PMID: 21268057
- PMCID: PMC3909029
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.22964
New insights into the inactivation of gastric tumor suppressor RUNX3: the role of H. pylori infection
Abstract
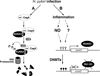
Runt-related transcription factor 3, or RUNX3, is a tumor suppressor in gastric cancer. Inactivation of RUNX3 is causally associated with the genesis of gastric cancer, since RUNX3 is frequently inactivated in gastric cancers by hemizygous deletion, hypermethylation of its promoter, or protein mislocalization. Infection with Helicobacter pylori is the strongest risk factor for the development of gastric cancer. Recent studies have indicated that H. pylori infection plays an important role in the inactivation of RUNX3, and that this inactivation contributes to the pathogenesis of H. pylori. Here we summarize these recent advances and discuss their significances in understanding the initiation and development of gastric cancer.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures
References
-
- Bae SC, Lee YH. Phosphorylation, acetylation and ubiquitination: the molecular basis of RUNX regulation. Gene. 2006;366:58–66. - PubMed
-
- Bornschein J, Rokkas T, Selgrad M, Malfertheiner P. Helicobacter pylori and clinical aspects of gastric cancer. Helicobacter. 2009;14(Suppl 1):41–45. - PubMed
-
- Chang TL, Ito K, Ko TK, Liu Q, Salto-Tellez M, Yeoh KG, Fukamachi H, Ito Y. Claudin-1 has tumor suppressive activity and is a direct target of RUNX3 in gastric epithelial cells. Gastroenterology. 2009 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

