Inducible expression of Runx2 results in multiorgan abnormalities in mice
- PMID: 21268087
- PMCID: PMC5079519
- DOI: 10.1002/jcb.22968
Inducible expression of Runx2 results in multiorgan abnormalities in mice
Abstract
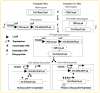
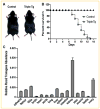
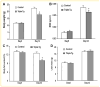
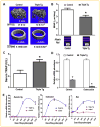
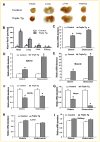
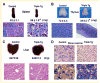
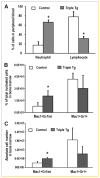
Runx2 is a transcription factor controlling skeletal development, and is also expressed in extraskeletal tissues where its function is not well understood. Existing Runx2 mutant and transgenic mouse models do not allow the necessary control of Runx2 expression to understand its functions in different tissues. We generated conditional, doxycyline-inducible, triple transgenic mice (CMV-Cre;ROSA26-neo(flox/+)-rtTA;Tet-O-Runx2) to investigate the effects of wide spread overexpression of Runx2. Osteoblasts isolated from CMV-Cre;ROSA26-neo(flox/+)-rtTA; Tet-O-Runx2 mice demonstrated a dose-dependent effect of doxycycline to stimulate Runx2 transgene expression. Doxycycline administration to CMV-Cre;ROSA26-neo(flox/+)-rtTA;Tet-O-Runx2 mice induced Runx2 transgene expression in all tissues tested, with the highest levels observed in kidney, ovary, and bone. Runx2 overexpression resulted in deceased body size and reduced viability. With regard to bone, Runx2 overexpressing mice paradoxically displayed profound osteopenia and diminished osteogenesis. Induced expression of Runx2 in extraskeletal tissues resulted in ectopic calcification and induction of the osteogenic program in a limited number of tissues, including lung and muscle. In addition, the triple transgenic mice showed evidence of a myeloproliferative disorder and an apparent inhibition of lymphocyte development. Thus, overexpression of Runx2 both within and outside of the skeleton can have diverse biological effects. Use of tissue specific Cre mice will allow this model to be used to conditionally and inducibly overexpress Runx2 in different tissues and provide a means to study the post-natal tissue- and cell context-dependent functions of Runx2.
Copyright © 2010 Wiley-Liss, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Ahn MY, Bae SC, Maruyama M, Ito Y. Comparison of the human genomic structure of the Runt domain-encoding PEBP2/CBFalpha gene family. Gene. 1996;168:279–280. - PubMed
-
- Banerjee C, Javed A, Choi JY, Green J, Rosen V, van Wijnen AJ, Stein JL, Lian JB, Stein GS. Differential regulation of the two principal Runx2/Cbfa1 n-terminal isoforms in response to bone morphogenetic protein-2 during development of the osteoblast phenotype. Endocrinology. 2001;142:4026–4039. - PubMed
-
- Bendayan D, Barziv Y, Kramer MR. Pulmonary calcifications: A review. Respir Med. 2000;94:190–193. - PubMed
-
- Blyth K, Terry A, Mackay N, Vaillant F, Bell M, Cameron ER, Neil JC, Stewart M. Runx2: A novel oncogenic effector revealed by in vivo complementation and retroviral tagging. Oncogene. 2001;20:295–302. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

