VennDiagram: a package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R
- PMID: 21269502
- PMCID: PMC3041657
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2105-12-35
VennDiagram: a package for the generation of highly-customizable Venn and Euler diagrams in R
Abstract
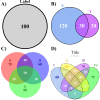
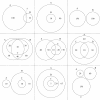
Background: Visualization of orthogonal (disjoint) or overlapping datasets is a common task in bioinformatics. Few tools exist to automate the generation of extensively-customizable, high-resolution Venn and Euler diagrams in the R statistical environment. To fill this gap we introduce VennDiagram, an R package that enables the automated generation of highly-customizable, high-resolution Venn diagrams with up to four sets and Euler diagrams with up to three sets.
Results: The VennDiagram package offers the user the ability to customize essentially all aspects of the generated diagrams, including font sizes, label styles and locations, and the overall rotation of the diagram. We have implemented scaled Venn and Euler diagrams, which increase graphical accuracy and visual appeal. Diagrams are generated as high-definition TIFF files, simplifying the process of creating publication-quality figures and easing integration with established analysis pipelines.
Conclusions: The VennDiagram package allows the creation of high quality Venn and Euler diagrams in the R statistical environment.
Figures

References
-
- Verhaak RG, Sanders MA, Bijl MA, Delwel R, Horsman S, Moorhouse MJ, van der Spek PJ, Lowenberg B, Valk PJ. HeatMapper: powerful combined visualization of gene expression profile correlations, genotypes, phenotypes and sample characteristics. BMC Bioinfo. 2006;7:337. doi: 10.1186/1471-2105-7-337. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Oliveros J. Venny. An interactive tool for comparing lists with Venn Diagrams. http://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index.html http://bioinfogp.cnb.csic.es/tools/venny/index.html
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

