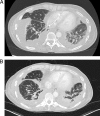
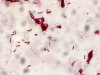
Gordonia bronchialis bacteremia and pleural infection: case report and review of the literature
- PMID: 21270217
- PMCID: PMC3122797
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02121-10
Gordonia bronchialis bacteremia and pleural infection: case report and review of the literature
Abstract
Gordonia species are aerobic actinomycetes recently recognized as causing human disease, often in the setting of intravascular catheter-related infections. We describe a case of Gordonia bronchialis bacteremia and pleural space infection in the absence of an indwelling intravascular catheter and review the breadth of reported infections with this emerging pathogen.
Figures
References
-
- Bakker X. R., Spauwen P. H., Dolmans W. M. 2004. Mycetoma of the hand caused by Gordona terrae: a case report. J. Hand Surg. Br. 29:188–190 - PubMed
-
- Blaschke A. J., et al. 2007. Gordonia species: emerging pathogens in pediatric patients that are identified by 16S ribosomal RNA gene sequencing. Clin. Infect. Dis. 45:483–486 - PubMed
-
- Buchman A. L., McNeil M. M., Brown J. M., Lasker B. A., Ament M. E. 1992. Central venous catheter sepsis caused by unusual Gordona (Rhodococcus) species: identification with a digoxigenin-labeled rDNA probe. Clin. Infect. Dis. 15:694–697 - PubMed
-
- Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute/NCCLS 2003. Susceptibility testing of mycobacteria, nocardiae, and other aerobic actinomycetes. Approved standard M24-A. National Committee for Clinical Laboratory Standards, Wayne, PA - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases