The expression and function of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in the embryonic mouse pancreas
- PMID: 21270265
- PMCID: PMC3028354
- DOI: 10.2337/db09-0035
The expression and function of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in the embryonic mouse pancreas
Abstract
Objective: Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP) is a member of a structurally related group of hormones that also includes glucagon, glucagon-like peptides, and secretin. GIP is an incretin, known to modulate glucose-induced insulin secretion. Recent studies have shown that glucagon is necessary for early insulin-positive differentiation, and a similar role for incretins in regulating embryonic insulin-positive differentiation seems probable. Here we studied the role of GIP signaling in insulin-positive differentiation in the embryonic mouse pancreas.
Research design and methods: The ontogeny of the GIP ligand and GIP receptor in the embryonic pancreas was investigated by immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR. GIP signaling was inhibited in cultured embryonic pancreata using morpholine-ring antisense against GIP ligand and receptor, or small interfering RNA (siRNA) for GIP ligand and receptor. Markers of endocrine cells and their progenitors were studied by immunohistochemistry and RT-PCR.
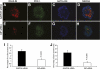
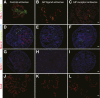
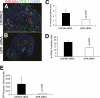
Results: GIP and GIP receptor mRNA were both detected in the embryonic pancreas by embryonic day 9.5 and then persisted throughout gestation. GIP was generally coexpressed with glucagon by immunostaining. The GIP receptor was typically coexpressed with insulin. Morpholine-ring antisense or siRNA against either GIP ligand or GIP receptor both inhibited the differentiation of insulin-positive cells. Inhibition of GIP or its receptor also led to a decrease in the number of Pdx-1-positive and sox9-positive cells in the cultured embryonic pancreas. The number of Pax6- and Nkx2.2-positive cells, representative of developing pancreatic endocrine cells and β-cells, respectively, was also decreased.
Conclusions: GIP signaling may play a role in early embryonic pancreas differentiation to form insulin-positive cells or β-cells.
Figures
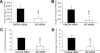
Similar articles
-
Expression of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide in the zebrafish.Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009 Dec;297(6):R1803-12. doi: 10.1152/ajpregu.00288.2009. Epub 2009 Sep 30. Am J Physiol Regul Integr Comp Physiol. 2009. PMID: 19793957 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide is expressed in pancreatic islet alpha-cells and promotes insulin secretion.Gastroenterology. 2010 May;138(5):1966-75. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2010.01.049. Epub 2010 Feb 4. Gastroenterology. 2010. PMID: 20138041
-
Enhanced glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide secretion and insulinotropic action in glucagon-like peptide 1 receptor -/- mice.Diabetes. 1998 Jul;47(7):1046-52. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.47.7.1046. Diabetes. 1998. PMID: 9648827
-
GIP and GLP-1 as incretin hormones: lessons from single and double incretin receptor knockout mice.Regul Pept. 2005 Jun 15;128(2):125-34. doi: 10.1016/j.regpep.2004.07.019. Regul Pept. 2005. PMID: 15780432 Review.
-
Glucose-dependent Insulinotropic Polypeptide (GIP): From prohormone to actions in endocrine pancreas and adipose tissue.Dan Med Bull. 2011 Dec;58(12):B4368. Dan Med Bull. 2011. PMID: 22142579 Review.
Cited by
-
Glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP).Mol Metab. 2025 May;95:102118. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2025.102118. Epub 2025 Feb 28. Mol Metab. 2025. PMID: 40024571 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of genetic variants of the incretin-related genes with quantitative traits and occurrence of type 2 diabetes in Japanese.Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2014 Aug 28;1:350-361. doi: 10.1016/j.ymgmr.2014.07.009. eCollection 2014. Mol Genet Metab Rep. 2014. PMID: 27896108 Free PMC article.
-
Smad signaling pathways regulate pancreatic endocrine development.Dev Biol. 2013 Jun 15;378(2):83-93. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2013.04.003. Epub 2013 Apr 17. Dev Biol. 2013. PMID: 23603491 Free PMC article.
-
Ectopic expression of GIP in pancreatic β-cells maintains enhanced insulin secretion in mice with complete absence of proglucagon-derived peptides.Diabetes. 2013 Feb;62(2):510-8. doi: 10.2337/db12-0294. Epub 2012 Oct 25. Diabetes. 2013. PMID: 23099862 Free PMC article.
-
Carbohydrate-induced secretion of glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide and glucagon-like peptide-1.J Diabetes Investig. 2016 Apr;7 Suppl 1(Suppl 1):27-32. doi: 10.1111/jdi.12449. Epub 2016 Mar 14. J Diabetes Investig. 2016. PMID: 27186352 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Creutzfeldt W. The incretin concept today. Diabetologia 1979;16:75–85 - PubMed
-
- Unger RH, Eisentraut AM. Entero-insular axis. Arch Intern Med 1969;123:261–266 - PubMed
-
- Efendic S, Portwood N. Overview of incretin hormones. Horm Metab Res 2004;36:742–746 - PubMed
-
- Yip RG, Wolfe MM. GIP biology and fat metabolism. Life Sci 2000;66:91–103 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

