Multiple faces of FoxM1 transcription factor: lessons from transgenic mouse models
- PMID: 21270518
- PMCID: PMC3115014
- DOI: 10.4161/cc.10.3.14709
Multiple faces of FoxM1 transcription factor: lessons from transgenic mouse models
Abstract
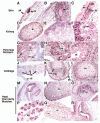
FoxM1 transcription factor (previously called HFH-11B, Trident, FoxM1b, Win, and MPP2) is expressed in actively dividing cells and critical for cell cycle progression. FoxM1 expression is induced in a variety of tissues during embryogenesis, and Foxm1 (-/-) mice exhibit embryonic lethal phenotype due to multiple abnormalities in the liver, heart, lung and blood vessels. FoxM1 levels are dramatically decreased in adult tissues, but FoxM1 expression is re-activated during organ injury and numerous cancers. In this review, we discussed the role of FoxM1 in different cell lineages using recent data from transgenic mouse models with conditional "gain-of-function" and "loss-of-function" of FoxM1, as well as tissue samples from human patients. In addition, we provided experimental data showing additional sites of FoxM1 expression in the mouse embryo. Novel cell-autonomous roles of FoxM1 in embryonic development, organ injury and cancer formation in vivo were analyzed. Potential application of these findings for the diagnosis and treatment of human diseases were discussed.
Figures
References
-
- Clark KL, Halay ED, Lai E, Burley SK. Co-crystal structure of the HNF-3/fork head DNA-recognition motif resembles histone H5. Nature. 1993;364:412–420. - PubMed
-
- Weigel D, Jurgens G, Kuttner F, Seifert E, Jackle H. The homeotic gene fork head encodes a nuclear protein and is expressed in the terminal regions of the Drosophila embryo. Cell. 1989;57:645–658. - PubMed
-
- Kaestner KH, Knochel W, Martinez DE. Unified nomenclature for the winged helix/forkhead transcription factors. Genes Dev. 2000;14:142–146. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
