Hippocampus, amygdala, and stress: interacting systems that affect susceptibility to addiction
- PMID: 21272015
- PMCID: PMC3141575
- DOI: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.2010.05896.x
Hippocampus, amygdala, and stress: interacting systems that affect susceptibility to addiction
Abstract
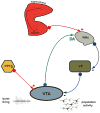
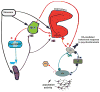
Stress is one of the major factors in drug abuse, particularly in relapse and drug-seeking behavior. However, the mechanisms underlying the interactions between stress and drug abuse are unclear. For many years, studies have focused on the role of the dopaminergic reward system in drug abuse. Our results, for example, show that increased dopaminergic activity is induced by drug sensitization and different stressors via potentiation of the ventral subiculum-nucleus accumbens (NAc) pathway. Although the role of the norepinephrine (NE) system in stress is well known, its involvement in drug abuse has received less attention. This review explores the different mechanisms by which stressors can modulate the ventral subiculum-accumbens pathway, and how these modulations can induce alterations in the behavioral response to drug administration. In particular, we will focus on two main afferents to the NAc, the basolateral amygdala and the ventral subiculum of the hippocampus, and their interactions with the locus coeruleus-norepinephrine system.
© 2011 New York Academy of Sciences.
Figures
References
-
- Deadwyler SA. Electrophysiological correlates of abused drugs: relation to natural rewards. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 2010;1187:140–7. - PubMed
-
- Koob GF, Le Moal M. Drug addiction, dysregulation of reward, and allostasis. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2001;24:97–129. - PubMed
-
- Wise RA, Rompre PP. Brain dopamine and reward. Annu Rev Psychol. 1989;40:191–225. - PubMed
-
- Schultz W. Predictive reward signal of dopamine neurons. J Neurophysiol. 1998;80:1–27. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

